| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sometimes, when the probability problems are complex, it can be helpful to graph the situation. Tree diagrams and Venn diagrams are two tools that can be used to visualize and solve conditional probabilities.
A tree diagram is a special type of graph used to determine the outcomes of an experiment. It consists of "branches" that are labeled with either frequencies or probabilities. Tree diagrams can make some probability problems easier to visualize and solve. The following example illustrates how to use a tree diagram.
In an urn, there are 11 balls. Three balls are red ( R ) and eight balls are blue ( B ). Draw two balls, one at a time, with replacement . "With replacement" means that you put the first ball back in the urn before you select the second ball. The tree diagram using frequencies that show all the possible outcomes follows.
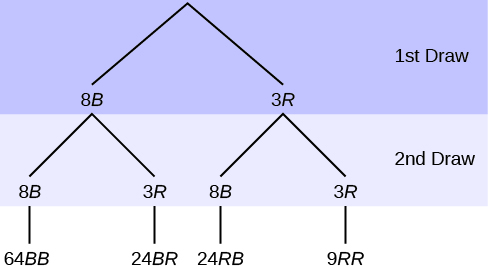
The first set of branches represents the first draw. The second set of branches represents the second draw. Each of the outcomes is distinct. In fact, we can list each red ball as R 1, R 2, and R 3 and each blue ball as B 1, B 2, B 3, B 4, B 5, B 6, B 7, and B 8. Then the nine RR outcomes can be written as:
The other outcomes are similar.
There are a total of 11 balls in the urn. Draw two balls, one at a time, with replacement. There are 11(11) = 121 outcomes, the size of the
sample space .
a. List the 24 BR outcomes: B 1 R 1, B 1 R 2, B 1 R 3, ...
a.
b. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( RR ).
b.
P (
RR ) =
=
c. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( RB OR BR ).
c.
P (
RB OR
BR ) =
+
=
d. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( R on 1st draw AND B on 2nd draw).
d.
P (
R on 1st draw AND
B on 2nd draw) =
P (
RB ) =
=
e. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( R on 2nd draw GIVEN B on 1st draw).
e. P ( R on 2nd draw GIVEN B on 1st draw) = P ( R on 2nd| B on 1st) = =
This problem is a conditional one. The sample space has been reduced to those outcomes that already have a blue on the first draw. There are 24 + 64 = 88 possible outcomes (24
BR and 64
BB ). Twenty-four of the 88 possible outcomes are
BR .
=
.
f. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( BB ).
f.
P (
BB ) =
g. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( B on the 2nd draw given R on the first draw).
g. P ( B on 2nd draw| R on 1st draw) =
There are 9 + 24 outcomes that have R on the first draw (9 RR and 24 RB ). The sample space is then 9 + 24 = 33. 24 of the 33 outcomes have B on the second draw. The probability is then .
In a standard deck, there are 52 cards. 12 cards are face cards (event F ) and 40 cards are not face cards (event N ). Draw two cards, one at a time, with replacement. All possible outcomes are shown in the tree diagram as frequencies. Using the tree diagram, calculate P ( FF ).
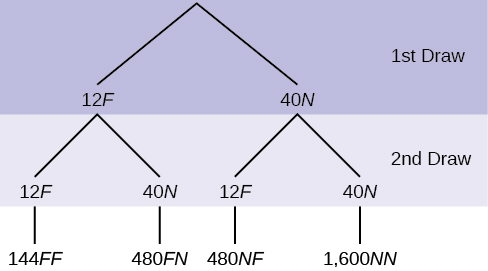
Total number of outcomes is 144 + 480 + 480 + 1600 = 2,704.
P ( FF ) =
An urn has three red marbles and eight blue marbles in it. Draw two marbles, one at a time, this time without replacement, from the urn. "Without replacement" means that you do not put the first ball back before you select the second marble. Following is a tree diagram for this situation. The branches are labeled with probabilities instead of frequencies. The numbers at the ends of the branches are calculated by multiplying the numbers on the two corresponding branches, for example, .
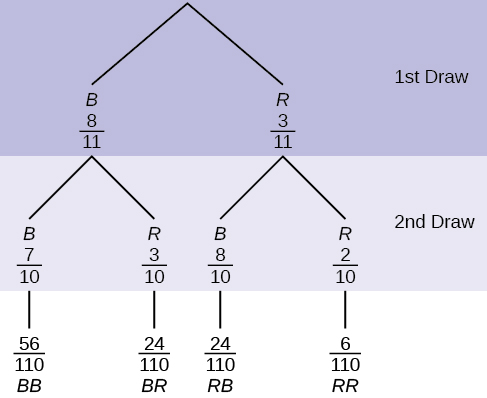
If you draw a red on the first draw from the three red possibilities, there are two red marbles left to draw on the second draw. You do not put back or replace the first marble after you have drawn it. You draw without replacement , so that on the second draw there are ten marbles left in the urn.
Calculate the following probabilities using the tree diagram.
b. Fill in the blanks:
P ( RB OR BR ) =
b.
P (
RB OR
BR ) =
+
=
d. Fill in the blanks.
P ( R on 1st AND B on 2nd) = P ( RB ) = (___)(___) =
d.
P (
R on 1st AND
B on 2nd) =
P (
RB ) =
=
f. Find P ( B on 2nd| R on 1st).
f. Using the tree diagram, P ( B on 2nd| R on 1st) = P ( R | B ) = .
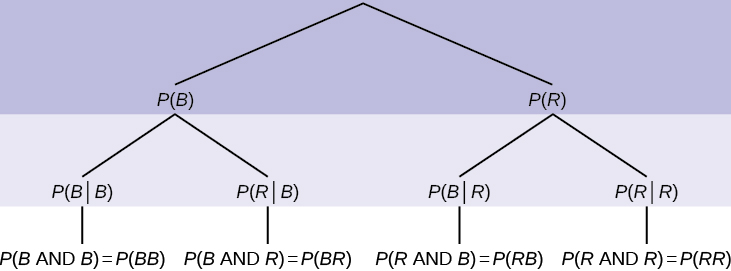
If we are using probabilities, we can label the tree in the following general way.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?