| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is important for you to understand when to use the CLT . If you are being asked to find the probability of the mean, use the CLT for the mean. If youare being asked to find the probability of a sum or total, use the CLT for sums. This also applies to percentiles for means and sums.
Law of Large Numbers
The Law of Large Numbers says that if you take samples of larger and larger size from any population, then the mean of the sample tends to get closer and closer to . From the Central Limit Theorem, we know that as gets larger and larger, the sample means follow a normal distribution. The larger n gets, the smaller thestandard deviation gets. (Remember that the standard deviation for is .) This means that the sample mean must be close to the population mean . We can say that is the value that the sample means approach as gets larger. The Central Limit Theorem illustrates the Law of Large Numbers.
Central Limit Theorem for the Mean and Sum Examples
A study involving stress is done on a college campus among the students. The stress scores follow a uniform distribution with the lowest stress score equal to 1 and the highest equal to 5. Using a sample of 75 students, find:
Let = one stress score.
Problems 1. and 2. ask you to find a probability or a percentile for a mean . Problems 3 and 4 ask you to find a probability or a percentile for a total or sum . The sample size, , is equal to 75.
Since the individual stress scores follow a uniform distribution, ~ where and (See Continuous Random Variables for the uniform).
For problems 1. and 2., let = the mean stress score for the 75 students. Then,
~ where .
Find . Draw the graph.
The probability that the mean stress score is lessthan 2 is about 0.
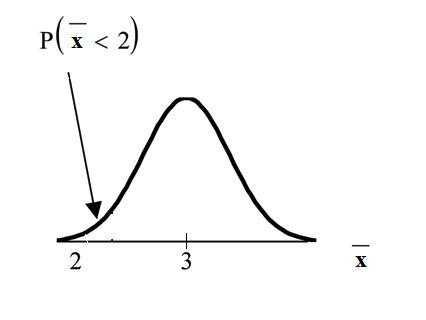
normalcdf
Find the 90th percentile for the mean of 75 stress scores. Draw a graph.
Let = the 90th precentile.
Find where .
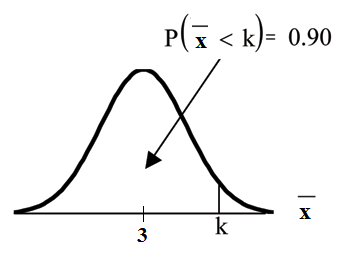
The 90th percentile for the mean of 75 scores is about 3.2. This tells us that 90% of all the means of 75 stress scores are at most 3.2 and 10% are at least3.2.
invNorm
For problems c and d, let = the sum of the 75 stress scores. Then, ~
Find . Draw the graph.
The mean of the sum of 75 stress scores is
The standard deviation of thesum of 75 stress scores is
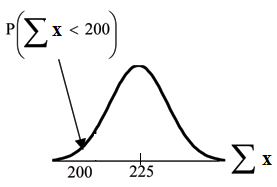
The probability that the total of 75 scores is less than 200 is about 0.
normalcdf
.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Collaborative statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?