| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You are president of an on-campus special events organization. You need a committee of seven students to plan a special birthday party for the president of the college. Your organization consists of 18 women and 15 men. You are interested in the number of men on your committee. If the members of the committee are randomly selected, what is the probability that your committee has more than four men?
This is a hypergeometric problem because you are choosing your committee from two groups (men and women).
e. Let X = _________ on the committee. What values does X take on?
e. Let
X =
the number of men on the committee.
x = 0, 1, 2, …, 7.
A palette has 200 milk cartons. Of the 200 cartons, it is known that ten of them have leaked and cannot be sold. A stock clerk randomly chooses 18 for inspection. He wants to know the probability that among the 18, no more than two are leaking. Give five reasons why this is a hypergeometric problem.
X ~ H ( r , b , n )
Read this as " X is a random variable with a hypergeometric distribution." The parameters are r , b , and n ; r = the size of the group of interest (first group), b = the size of the second group, n = the size of the chosen sample.
A school site committee is to be chosen randomly from six men and five women. If the committee consists of four members chosen randomly, what is the probability that two of them are men? How many men do you expect to be on the committee?
Let X = the number of men on the committee of four. The men are the group of interest (first group).
X takes on the values 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, where r = 6 , b = 5 , and n = 4 . X ~ H (6, 5, 4)
Find P ( x = 2). P ( x = 2) = 0.4545 (calculator or computer)
Currently, the TI-83+ and TI-84 do not have hypergeometric probability functions. There are a number of computer packages, including Microsoft Excel, that do.
The probability that there are two men on the committee is about 0.45.
The graph of X ~ H (6, 5, 4) is:
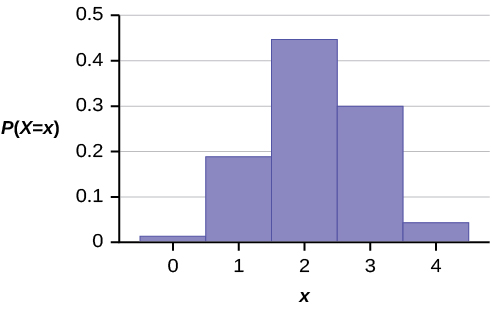
The y -axis contains the probability of X , where X = the number of men on the committee.
You would expect m = 2.18 (about two) men on the committee.
The formula for the mean is
An intramural basketball team is to be chosen randomly from 15 boys and 12 girls. The team has ten slots. You want to know the probability that eight of the players will be boys. What is the group of interest and the sample?
The group of interest is the 15 boys. The sample consists of the ten slots on the intramural basketball team.
A hypergeometric experiment is a statistical experiment with the following properties:
The outcomes of a hypergeometric experiment fit a hypergeometric probability distribution. The random variable
X = the number of items from the group of interest. The distribution of
X is denoted
X ~
H (
r ,
b ,
n ), where
r = the size of the group of interest (first group),
b = the size of the second group, and
n = the size of the chosen sample. It follows that
n ≤
r +
b . The mean of
X is
μ =
and the standard deviation is
σ =
.
X ~ H ( r , b , n ) means that the discrete random variable X has a hypergeometric probability distribution with r = the size of the group of interest (first group), b = the size of the second group, and n = the size of the chosen sample.
X = the number of items from the group of interest that are in the chosen sample, and X may take on the values x = 0, 1, ..., up to the size of the group of interest. (The minimum value for X may be larger than zero in some instances.)
n ≤ r + b
The mean of X is given by the formula μ = and the standard deviation is = .
Use the following information to answer the next five exercises: Suppose that a group of statistics students is divided into two groups: business majors and non-business majors. There are 16 business majors in the group and seven non-business majors in the group. A random sample of nine students is taken. We are interested in the number of business majors in the sample.
In words, define the random variable X .
X = the number of business majors in the sample.
X ~ _____(_____,_____)
Find the standard deviation.
On average ( μ ), how many would you expect to be business majors?
6.26

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?