| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The expected percentage of the number of pets students have in their homes is distributed (this is the given distribution for the student population of the United States) as in [link] .
| Number of Pets | Percent |
|---|---|
| 0 | 18 |
| 1 | 25 |
| 2 | 30 |
| 3 | 18 |
| 4+ | 9 |
A random sample of 1,000 students from the Eastern United States resulted in the data in [link] .
| Number of Pets | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 0 | 210 |
| 1 | 240 |
| 2 | 320 |
| 3 | 140 |
| 4+ | 90 |
At the 1% significance level, does it appear that the distribution “number of pets” of students in the Eastern United States is different from the distribution for the United States student population as a whole? What is the p -value?
p -value = 0.0036
We reject the null hypothesis that the distributions are the same. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the distribution “number of pets” of students in the Eastern United States is different from the distribution for the United States student population as a whole.
Suppose you flip two coins 100 times. The results are 20 HH , 27 HT , 30 TH , and 23 TT . Are the coins fair? Test at a 5% significance level.
This problem can be set up as a goodness-of-fit problem. The sample space for flipping two fair coins is { HH , HT , TH , TT }. Out of 100 flips, you would expect 25 HH , 25 HT , 25 TH , and 25 TT . This is the expected distribution. The question, "Are the coins fair?" is the same as saying, "Does the distribution of the coins (20 HH , 27 HT , 30 TH , 23 TT ) fit the expected distribution?"
Random Variable: Let X = the number of heads in one flip of the two coins. X takes on the values 0, 1, 2. (There are 0, 1, or 2 heads in the flip of two coins.) Therefore, the number of cells is three . Since X = the number of heads, the observed frequencies are 20 (for two heads), 57 (for one head), and 23 (for zero heads or both tails). The expected frequencies are 25 (for two heads), 50 (for one head), and 25 (for zero heads or both tails). This test is right-tailed.
H 0 : The coins are fair.
H a : The coins are not fair.
Distribution for the test: where df = 3 – 1 = 2.
Calculate the test statistic: χ 2 = 2.14
Graph:
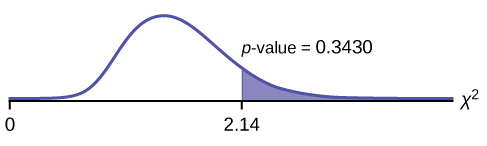
Probability statement: p -value = P ( χ 2 >2.14) = 0.3430
Compare α and the p -value:
Make a decision: Since α < p -value, do not reject H 0 .
Conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the coins are not fair.
Press
STAT and
ENTER . Make sure you
clear lists
L1 ,
L2 , and
L3 if they have data in them. Into
L1 , put the observed
frequencies
20 ,
57 ,
23 . Into
L2 , put the expected frequencies
25 ,
50 ,
25 . Arrow
over to list
L3 and up to the name area
"L3" . Enter
(L1-L2)^2/L2 and
ENTER . Press
2nd QUIT . Press
2nd LIST and arrow over to
MATH . Press
5 . You should see
"sum" .
Enter L3 . Rounded to two decimal places, you
should see
2.14 . Press
2nd DISTR . Arrow down to
7:χ2cdf (or press
7 ). Press
ENTER . Enter
2.14,1E99,2) . Rounded to four places, you should see
.3430 , which
is the p-value.
The newer TI-84 calculators have in
STAT TESTS the test
Chi2 GOF . To run the test, put the observed values (the data) into a first list and the expected values (the values you expect if the null hypothesis is true) into a second list. Press
STAT TESTS and
Chi2 GOF . Enter the list names for the Observed list and the Expected list. Enter the degrees of freedom and press
calculate or
draw . Make
sure you clear any lists before you start.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?