| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
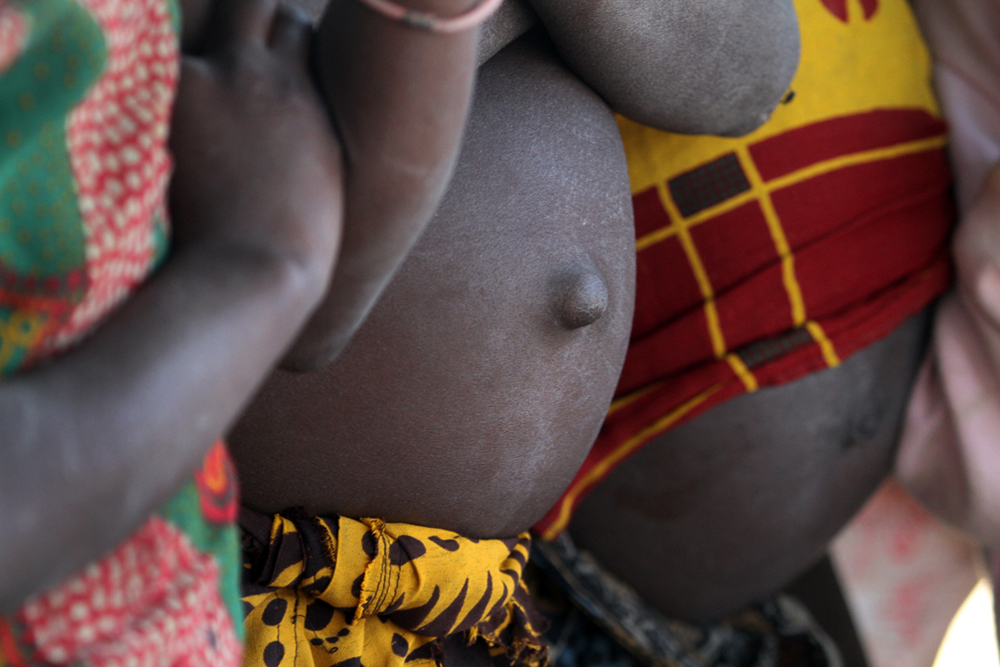
In peripheral nations with low per capita income, it is not the cost of healthcare that is the most pressing concern. Rather, low-income countries must manage such problems as infectious disease, high infant mortality rates, scarce medical personnel, and inadequate water and sewer systems. Such issues, which high-income countries rarely even think about, are central to the lives of most people in low-income nations. Due to such health concerns, low-income nations have higher rates of infant mortality and lower average life spans.
One of the biggest contributors to medical issues in low-income countries is the lack of access to clean water and basic sanitation resources. According to a 2014 UNICEF report, almost half of the developing world’s population lacks improved sanitation facilities. The World Health Organization (WHO) tracks health-related data for 193 countries. In their 2011 World Health Statistics report, they document the following statistics:
Social epidemiology is the study of the causes and distribution of diseases. From a global perspective, the health issues of high-income nations tend toward diseases like cancer as well as those that are linked to obesity, like heart disease, diabetes, and musculoskeletal disorders. Low-income nations are more likely to contend with infectious disease, high infant mortality rates, scarce medical personnel, and inadequate water and sanitation systems.
If social epidemiologists studied the United States in the colonial period, what differences would they find between now and then?
What do you think are some of the contributing factors to obesity-related diseases in the United States?
Study this map on global life expectancies: (External Link) . What trends do you notice?
Bromet et al. 2011. “Cross-National Epidemiology of DSM-IV Major Depressive Episode.” BMC Medicine 9:90. Retrieved December 12, 2011 ( (External Link) ).
Huffman, Wallace E., Sonya Kostova Huffman, AbebayehuTegene, and KyrreRickertsen. 2006. “The Economics of Obesity-Related Mortality among High Income Countries” International Association of Agricultural Economists. Retrieved December 12, 2011 ( (External Link) ).
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. 2011. Health at a Glance 2011: OECD Indicators . OECD Publishing. Retrieved December 12, 2011 ( (External Link) ).
UNICEF. 2011. “Water, Sanitation and Hygiene.” Retrieved December 12, 2011 ( (External Link) ).
World Health Organization. 2011. “World Health Statistics 2011.” Retrieved December 12, 2011 ( (External Link) ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to sociology 2e' conversation and receive update notifications?