| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are several positive aspects of bureaucracies. They are intended to improve efficiency, ensure equal opportunities, and ensure that most people can be served. And there are times when rigid hierarchies are needed. But remember that many of our bureaucracies grew large at the same time that our school model was developed––during the Industrial Revolution. Young workers were trained, and organizations were built for mass production, assembly line work, and factory jobs. In these scenarios, a clear chain of command was critical. Now, in the information age, this kind of rigid training and adherence to protocol can actually decrease both productivity and efficiency.
Today’s workplace requires a faster pace, more problem solving, and a flexible approach to work. Too much adherence to explicit rules and a division of labor can leave an organization behind. And unfortunately, once established, bureaucracies can take on a life of their own. Maybe you have heard the expression “trying to turn a tanker around mid-ocean,” which refers to the difficulties of changing direction with something large and set in its ways. State governments and current budget crises are examples of this challenge. It is almost impossible to make quick changes, leading states to continue, year after year, with increasingly unbalanced budgets. Finally, bureaucracies, as mentioned, grew as institutions at a time when privileged white males held all the power. While ostensibly based on meritocracy, bureaucracies can perpetuate the existing balance of power by only recognizing the merit in traditionally male and privileged paths.
Michels (1911) suggested that all large organizations are characterized by the Iron Rule of Oligarchy , wherein an entire organization is ruled by a few elites. Do you think this is true? Can a large organization be collaborative?

The McDonaldization of Society (Ritzer 1993) refers to the increasing presence of the fast food business model in common social institutions. This business model includes efficiency (the division of labor), predictability, calculability, and control (monitoring). For example, in your average chain grocery store, people at the register check out customers while stockers keep the shelves full of goods and deli workers slice meats and cheese to order (efficiency). Whenever you enter a store within that grocery chain, you receive the same type of goods, see the same store organization, and find the same brands at the same prices (predictability). You will find that goods are sold by the pound, so that you can weigh your fruit and vegetable purchase rather than simply guessing at the price for that bag of onions, while the employees use a timecard to calculate their hours and receive overtime pay (calculability). Finally, you will notice that all store employees are wearing a uniform (and usually a name tag) so that they can be easily identified. There are security cameras to monitor the store, and some parts of the store, such as the stockroom, are generally considered off-limits to customers (control). While McDonaldization has resulted in improved profits and an increased availability of various goods and services to more people worldwide, it has also reduced the variety of goods available in the marketplace while rendering available products uniform, generic, and bland. Think of the difference between a mass-produced shoe and one made by a local cobbler, between a chicken from a family-owned farm and a corporate grower, or between a cup of coffee from the local diner and one from Starbucks.
We often talk about bureaucracies disparagingly, and no organization takes more heat than fast food restaurants. Several books and movies, such as Fast Food Nation: The Dark Side of the All-American Meal by Eric Schossler, paint an ugly picture of what goes in, what goes on, and what comes out of fast food chains. From their environmental impact to their role in the U.S. obesity epidemic, fast food chains are connected to numerous societal ills. Furthermore, working at a fast food restaurant is often disparaged, and even referred to dismissively, as having a McJob rather than a real job.
But business school professor Jerry Newman went undercover and worked behind the counter at seven fast food restaurants to discover what really goes on there. His book, My Secret Life on the McJob , documents his experience. Unlike Schossler, Newman found that these restaurants offer much good alongside the bad. Specifically, he asserted that the employees were honest and hardworking, that management was often impressive, and that the jobs required a lot more skill and effort than most people imagined. In the book, Newman cites a pharmaceutical executive who says a fast-food service job on an applicant’s résumé is a plus because it indicates the employee is reliable and can handle pressure.
Businesses like Chipotle, Panera, and Costco attempt to combat many of the effects of McDonaldization. In fact, Costco is known for paying its employees an average of $20 per hour, or slightly more than $40,000.00 per year. Nearly 90% of their employees receive health insurance from Costco, a number that is unheard of in the retail sector.
While Chipotle is not known for high wages of its employees, it is known for attempting to sell high-quality foods from responsibly sourced providers. This is a different approach from what Schossler describes among burger chains like McDonalds.
So what do you think? Are these McJobs and the organizations that offer them still serving a role in the economy and people’s careers? Or are they dead-end jobs that typify all that is negative about large bureaucracies? Have you ever worked in one? Would you?
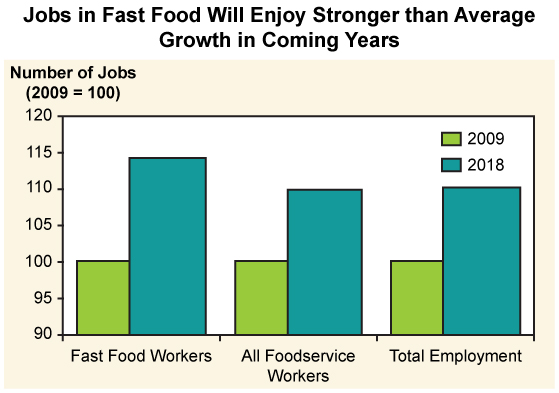
Large organizations fall into three main categories: normative/voluntary, coercive, and utilitarian. We live in a time of contradiction: while the pace of change and technology are requiring people to be more nimble and less bureaucratic in their thinking, large bureaucracies like hospitals, schools, and governments are more hampered than ever by their organizational format. At the same time, the past few decades have seen the development of a trend to bureaucratize and conventionalize local institutions. Increasingly, Main Streets across the country resemble each other; instead of a Bob’s Coffee Shop and Jane’s Hair Salon there is a Dunkin Donuts and a Supercuts. This trend has been referred to as the McDonaldization of society.
What do you think about the recent spotlight on fast food restaurants? Do you think they contribute to society’s ills? Do you believe they provide a needed service? Have you ever worked a job like this? What did you learn?
Do you consider today’s large companies like General Motors, Amazon, or Facebook to be bureaucracies? Why, or why not? Which of the main characteristics of bureaucracies do you see in them? Which are absent?
Where do you prefer to shop, eat out, or grab a cup of coffee? Large chains like Walmart or smaller retailers? Starbucks or a local restaurant? What do you base your decisions on? Does this section change how you think about these choices? Why, or why not?
As mentioned above, the concept of McDonaldization is a growing one. The following link discusses this phenomenon further: (External Link)
Di Meglio, Francesca. 2007. “Learning on the McJob.” Bloomberg Businessweek , March 22. Retrieved February 10, 2012 ( (External Link) ).
Etzioni, Amitai. 1975. A Comparative Analysis of Complex Organizations: On Power, Involvement, and Their Correlates . New York: Free Press.
Goffman, Erving. 1961. Asylums: Essays on the Social Situation of Mental Patients and Other Inmates . Chicago, IL: Aldine.
Michels, Robert. 1949 [1911]. Political Parties . Glencoe, IL: Free Press.
Newman, Jerry. 2007. My Secret Life on the McJob . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Ritzer, George. 1993. The McDonaldization of Society . Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge.
Schlosser, Eric. 2001. Fast Food Nation: The Dark Side of the All-American Meal . Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
United States Department of Labor. Bureau of Labor Statistics Occupational Outlook Handbook, 2010–2011 Edition. Retrieved February 10, 2012 ( (External Link) ).
Weber, Max. 1968 [1922]. Economy and Society: An Outline of Interpretative Sociology . New York: Bedminster.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to sociology 2e' conversation and receive update notifications?