| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
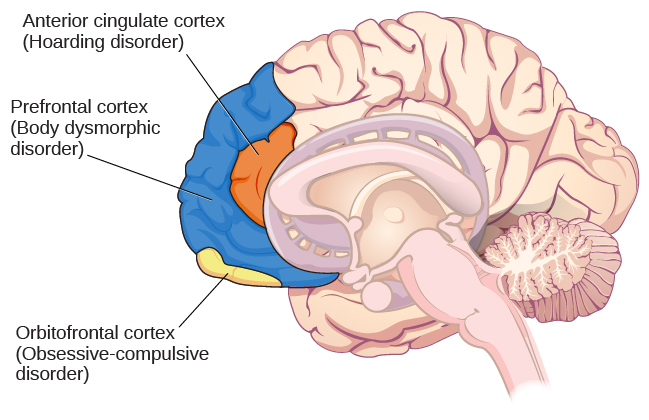
A brain region that is believed to play a critical role in OCD is the orbitofrontal cortex (Kopell&Greenberg, 2008), an area of the frontal lobe involved in learning and decision-making (Rushworth, Noonan, Boorman, Walton,&Behrens, 2011) ( [link] ). In people with OCD, the orbitofrontal cortex becomes especially hyperactive when they are provoked with tasks in which, for example, they are asked to look at a photo of a toilet or of pictures hanging crookedly on a wall (Simon, Kaufmann, Müsch, Kischkel,&Kathmann, 2010). The orbitofrontal cortex is part of a series of brain regions that, collectively, is called the OCD circuit; this circuit consists of several interconnected regions that influence the perceived emotional value of stimuli and the selection of both behavioral and cognitive responses (Graybiel&Rauch, 2000). As with the orbitofrontal cortex, other regions of the OCD circuit show heightened activity during symptom provocation (Rotge et al., 2008), which suggests that abnormalities in these regions may produce the symptoms of OCD (Saxena, Bota,&Brody, 2001). Consistent with this explanation, people with OCD show a substantially higher degree of connectivity of the orbitofrontal cortex and other regions of the OCD circuit than do those without OCD (Beucke et al., 2013).
The findings discussed above were based on imaging studies, and they highlight the potential importance of brain dysfunction in OCD. However, one important limitation of these findings is the inability to explain differences in obsessions and compulsions. Another limitation is that the correlational relationship between neurological abnormalities and OCD symptoms cannot imply causation (Abramowitz&Siqueland, 2013).
The symptoms of OCD have been theorized to be learned responses, acquired and sustained as the result of a combination of two forms of learning: classical conditioning and operant conditioning (Mowrer, 1960; Steinmetz, Tracy,&Green, 2001). Specifically, the acquisition of OCD may occur first as the result of classical conditioning, whereby a neutral stimulus becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus that provokes anxiety or distress. When an individual has acquired this association, subsequent encounters with the neutral stimulus trigger anxiety, including obsessive thoughts; the anxiety and obsessive thoughts (which are now a conditioned response) may persist until she identifies some strategy to relieve it. Relief may take the form of a ritualistic behavior or mental activity that, when enacted repeatedly, reduces the anxiety. Such efforts to relieve anxiety constitute an example of negative reinforcement (a form of operant conditioning). Recall from the chapter on learning that negative reinforcement involves the strengthening of behavior through its ability to remove something unpleasant or aversive. Hence, compulsive acts observed in OCD may be sustained because they are negatively reinforcing, in the sense that they reduce anxiety triggered by a conditioned stimulus.
Suppose an individual with OCD experiences obsessive thoughts about germs, contamination, and disease whenever she encounters a doorknob. What might have constituted a viable unconditioned stimulus? Also, what would constitute the conditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, and conditioned response? What kinds of compulsive behaviors might we expect, and how do they reinforce themselves? What is decreased? Additionally, and from the standpoint of learning theory, how might the symptoms of OCD be treated successfully?
Obsessive-compulsive and related disorders are a group of DSM-5 disorders that overlap somewhat in that they each involve intrusive thoughts and/or repetitive behaviors. Perhaps the most recognized of these disorders is obsessive-compulsive disorder, in which a person is obsessed with unwanted, unpleasant thoughts and/or compulsively engages in repetitive behaviors or mental acts, perhaps as a way of coping with the obsessions. Body dysmorphic disorder is characterized by the individual becoming excessively preoccupied with one or more perceived flaws in his physical appearance that are either nonexistent or unnoticeable to others. Preoccupation with the perceived physical defects causes the person to experience significant anxiety regarding how he appears to others. Hoarding disorder is characterized by persistent difficulty in discarding or parting with objects, regardless of their actual value, often resulting in the accumulation of items that clutter and congest her living area.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?