| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
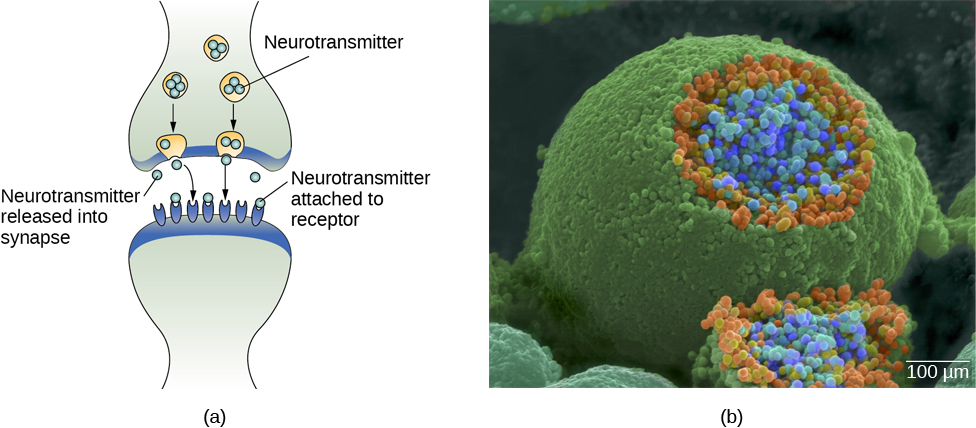
In healthy individuals, the neuronal signal moves rapidly down the axon to the terminal buttons, where synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapse ( [link] ). The synapse is a very small space between two neurons and is an important site where communication between neurons occurs. Once neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, they travel across the small space and bind with corresponding receptors on the dendrite of an adjacent neuron. Receptors , proteins on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach, vary in shape, with different shapes “matching” different neurotransmitters.
How does a neurotransmitter “know” which receptor to bind to? The neurotransmitter and the receptor have what is referred to as a lock-and-key relationship—specific neurotransmitters fit specific receptors similar to how a key fits a lock. The neurotransmitter binds to any receptor that it fits.
Now that we have learned about the basic structures of the neuron and the role that these structures play in neuronal communication, let’s take a closer look at the signal itself—how it moves through the neuron and then jumps to the next neuron, where the process is repeated.
We begin at the neuronal membrane. The neuron exists in a fluid environment—it is surrounded by extracellular fluid and contains intracellular fluid (i.e., cytoplasm). The neuronal membrane keeps these two fluids separate—a critical role because the electrical signal that passes through the neuron depends on the intra- and extracellular fluids being electrically different. This difference in charge across the membrane, called the membrane potential , provides energy for the signal.
The electrical charge of the fluids is caused by charged molecules (ions) dissolved in the fluid. The semipermeable nature of the neuronal membrane somewhat restricts the movement of these charged molecules, and, as a result, some of the charged particles tend to become more concentrated either inside or outside the cell.
Between signals, the neuron membrane’s potential is held in a state of readiness, called the resting potential . Like a rubber band stretched out and waiting to spring into action, ions line up on either side of the cell membrane, ready to rush across the membrane when the neuron goes active and the membrane opens its gates (i.e., a sodium-potassium pump that allows movement of ions across the membrane). Ions in high-concentration areas are ready to move to low-concentration areas, and positive ions are ready to move to areas with a negative charge.
In the resting state, sodium (Na + ) is at higher concentrations outside the cell, so it will tend to move into the cell. Potassium (K + ), on the other hand, is more concentrated inside the cell, and will tend to move out of the cell ( [link] ). In addition, the inside of the cell is slightly negatively charged compared to the outside. This provides an additional force on sodium, causing it to move into the cell.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?