| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sleep is not a uniform state of being. Instead, sleep is composed of several different stages that can be differentiated from one another by the patterns of brain wave activity that occur during each stage. These changes in brain wave activity can be visualized using EEG and are distinguished from one another by both the frequency and amplitude of brain waves ( [link] ). Sleep can be divided into two different general phases: REM sleep and non-REM (NREM) sleep. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep is characterized by darting movements of the eyes under closed eyelids. Brain waves during REM sleep appear very similar to brain waves during wakefulness. In contrast, non-REM (NREM) sleep is subdivided into four stages distinguished from each other and from wakefulness by characteristic patterns of brain waves. The first four stages of sleep are NREM sleep, while the fifth and final stage of sleep is REM sleep. In this section, we will discuss each of these stages of sleep and their associated patterns of brain wave activity.
The first stage of NREM sleep is known as stage 1 sleep. Stage 1 sleep is a transitional phase that occurs between wakefulness and sleep, the period during which we drift off to sleep. During this time, there is a slowdown in both the rates of respiration and heartbeat. In addition, stage 1 sleep involves a marked decrease in both overall muscle tension and core body temperature.
In terms of brain wave activity, stage 1 sleep is associated with both alpha and theta waves. The early portion of stage 1 sleep produces alpha waves , which are relatively low frequency (8–13Hz), high amplitude patterns of electrical activity (waves) that become synchronized ( [link] ). This pattern of brain wave activity resembles that of someone who is very relaxed, yet awake. As an individual continues through stage 1 sleep, there is an increase in theta wave activity. Theta waves are even lower frequency (4–7 Hz), higher amplitude brain waves than alpha waves. It is relatively easy to wake someone from stage 1 sleep; in fact, people often report that they have not been asleep if they are awoken during stage 1 sleep.
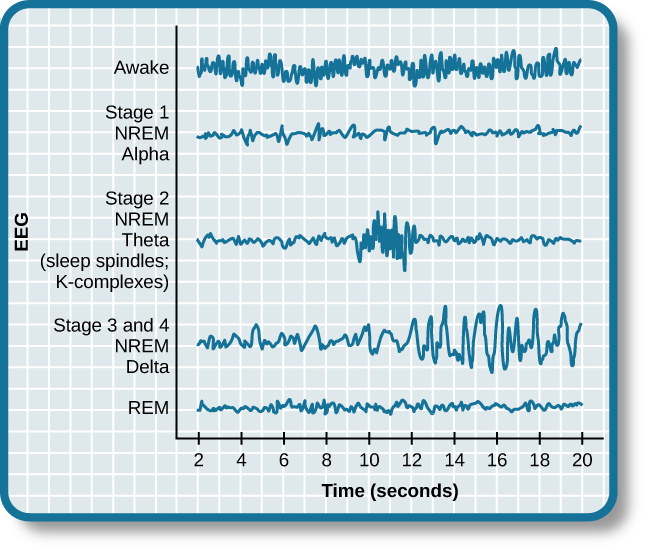
As we move into stage 2 sleep , the body goes into a state of deep relaxation. Theta waves still dominate the activity of the brain, but they are interrupted by brief bursts of activity known as sleep spindles ( [link] ). A sleep spindle is a rapid burst of higher frequency brain waves that may be important for learning and memory (Fogel&Smith, 2011; Poe, Walsh,&Bjorness, 2010). In addition, the appearance of K-complexes is often associated with stage 2 sleep. A K-complex is a very high amplitude pattern of brain activity that may in some cases occur in response to environmental stimuli. Thus, K-complexes might serve as a bridge to higher levels of arousal in response to what is going on in our environments (Halász, 1993; Steriade&Amzica, 1998).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?