| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like food, sex is an important part of our lives. From an evolutionary perspective, the reason is obvious—perpetuation of the species. Sexual behavior in humans, however, involves much more than reproduction. This section provides an overview of research that has been conducted on human sexual behavior and motivation. This section will close with a discussion of issues related to gender and sexual orientation.
Much of what we know about the physiological mechanisms that underlie sexual behavior and motivation comes from animal research. As you’ve learned, the hypothalamus plays an important role in motivated behaviors, and sex is no exception. In fact, lesions to an area of the hypothalamus called the medial preoptic area completely disrupt a male rat’s ability to engage in sexual behavior. Surprisingly, medial preoptic lesions do not change how hard a male rat is willing to work to gain access to a sexually receptive female ( [link] ). This suggests that the ability to engage in sexual behavior and the motivation to do so may be mediated by neural systems distinct from one another.

Animal research suggests that limbic system structures such as the amygdala and nucleus accumbens are especially important for sexual motivation. Damage to these areas results in a decreased motivation to engage in sexual behavior, while leaving the ability to do so intact ( [link] ) (Everett, 1990). Similar dissociations of sexual motivation and sexual ability have also been observed in the female rat (Becker, Rudick,&Jenkins, 2001; Jenkins&Becker, 2001).
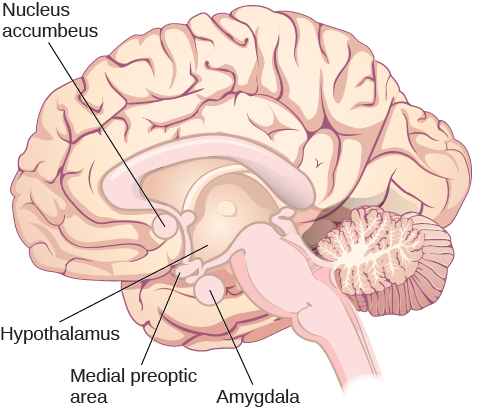
Although human sexual behavior is much more complex than that seen in rats, some parallels between animals and humans can be drawn from this research. The worldwide popularity of drugs used to treat erectile dysfunction (Conrad, 2005) speaks to the fact that sexual motivation and the ability to engage in sexual behavior can also be dissociated in humans. Moreover, disorders that involve abnormal hypothalamic function are often associated with hypogonadism (reduced function of the gonads) and reduced sexual function (e.g., Prader-Willi syndrome). Given the hypothalamus’s role in endocrine function, it is not surprising that hormones secreted by the endocrine system also play important roles in sexual motivation and behavior. For example, many animals show no sign of sexual motivation in the absence of the appropriate combination of sex hormones from their gonads. While this is not the case for humans, there is considerable evidence that sexual motivation for both men and women varies as a function of circulating testosterone levels (Bhasin, Enzlin, Coviello,&Basson, 2007; Carter, 1992; Sherwin, 1988).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?