| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A type of motion described as simple harmonic motion involves a restoring force but assumes that the motion will continue forever. Imagine a weighted object hanging on a spring, When that object is not disturbed, we say that the object is at rest, or in equilibrium. If the object is pulled down and then released, the force of the spring pulls the object back toward equilibrium and harmonic motion begins. The restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from its equilibrium point. When
We see that simple harmonic motion equations are given in terms of displacement:
where is the amplitude, is the period, and is the frequency, or the number of cycles per unit of time.
For the given functions,
In reality, a pendulum does not swing back and forth forever, nor does an object on a spring bounce up and down forever. Eventually, the pendulum stops swinging and the object stops bouncing and both return to equilibrium. Periodic motion in which an energy-dissipating force, or damping factor, acts is known as damped harmonic motion . Friction is typically the damping factor.
In physics, various formulas are used to account for the damping factor on the moving object. Some of these are calculus-based formulas that involve derivatives. For our purposes, we will use formulas for basic damped harmonic motion models.
In damped harmonic motion , the displacement of an oscillating object from its rest position at time is given as
where is a damping factor, is the initial displacement and is the period.
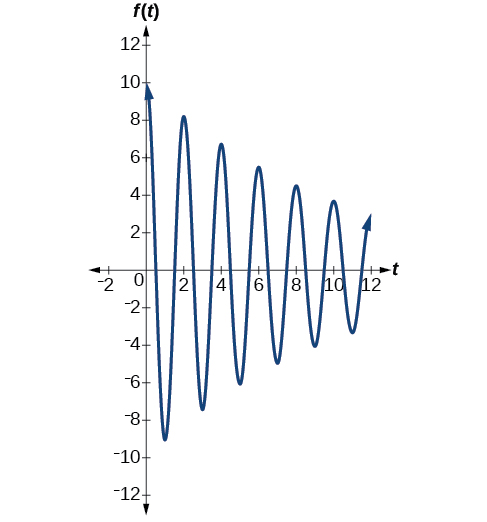
Model the equations that fit the two scenarios and use a graphing utility to graph the functions: Two mass-spring systems exhibit damped harmonic motion at a frequency of cycles per second. Both have an initial displacement of 10 cm. The first has a damping factor of and the second has a damping factor of
At time the displacement is the maximum of 10 cm, which calls for the cosine function. The cosine function will apply to both models.
We are given the frequency of 0.5 cycles per second. Thus,
The first spring system has a damping factor of Following the general model for damped harmonic motion, we have
[link] models the motion of the first spring system.
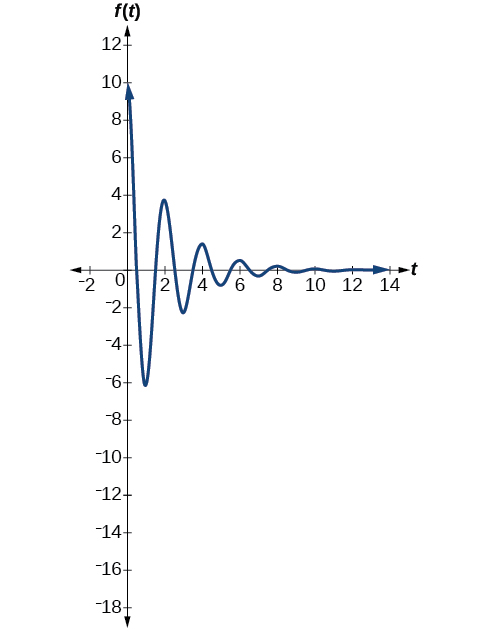
The second spring system has a damping factor of and can be modeled as
[link] models the motion of the second spring system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?