| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Graph Identify and label the focus, directrix, and endpoints of the latus rectum.
Focus: Directrix: Endpoints of the latus rectum:
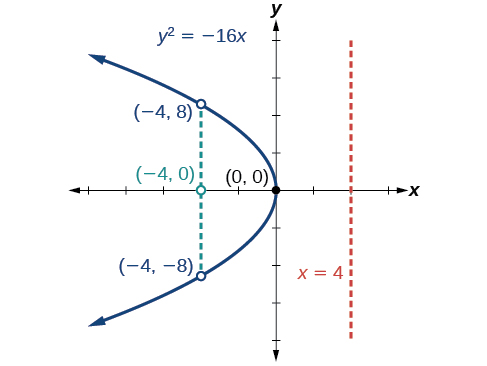
Graph Identify and label the focus , directrix , and endpoints of the latus rectum .
The standard form that applies to the given equation is Thus, the axis of symmetry is the y -axis. It follows that:
Next we plot the focus, directrix, and latus rectum, and draw a smooth curve to form the parabola .
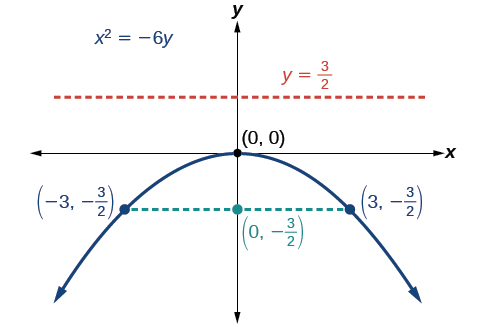
Graph Identify and label the focus, directrix, and endpoints of the latus rectum.
Focus: Directrix: Endpoints of the latus rectum:
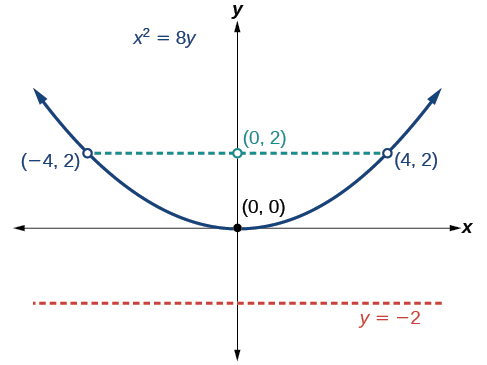
In the previous examples, we used the standard form equation of a parabola to calculate the locations of its key features. We can also use the calculations in reverse to write an equation for a parabola when given its key features.
Given its focus and directrix, write the equation for a parabola in standard form.
What is the equation for the parabola with focus and directrix
The focus has the form so the equation will have the form
Therefore, the equation for the parabola is
What is the equation for the parabola with focus and directrix
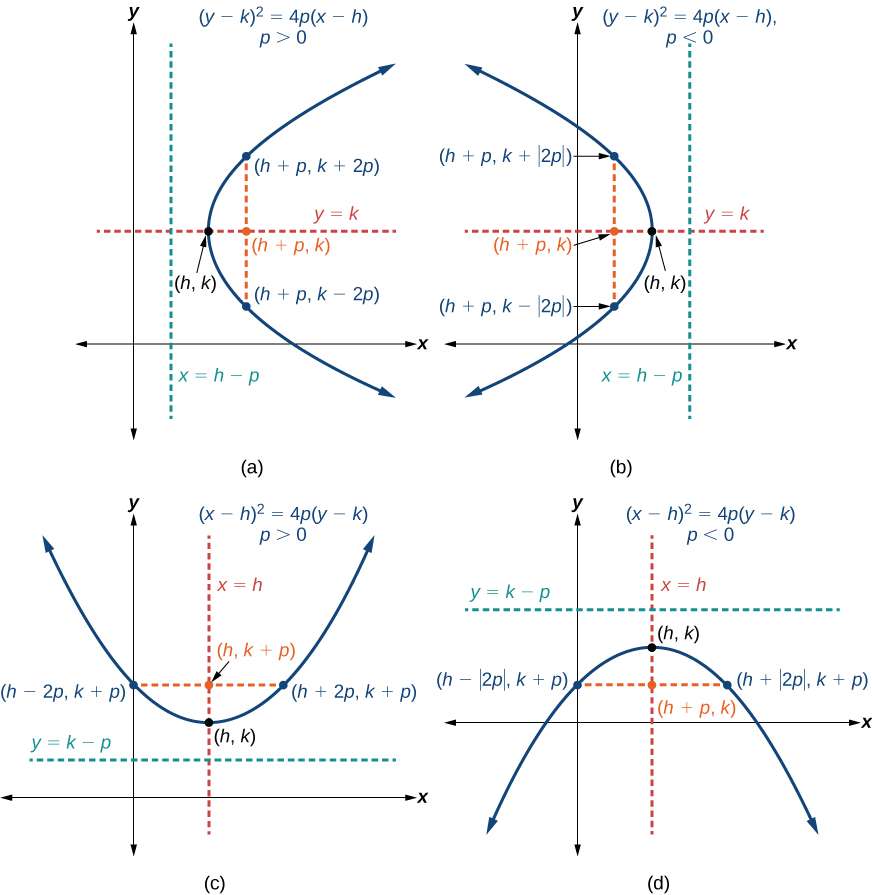
Like other graphs we’ve worked with, the graph of a parabola can be translated. If a parabola is translated units horizontally and units vertically, the vertex will be This translation results in the standard form of the equation we saw previously with replaced by and replaced by
To graph parabolas with a vertex other than the origin, we use the standard form for parabolas that have an axis of symmetry parallel to the x -axis, and for parabolas that have an axis of symmetry parallel to the y -axis. These standard forms are given below, along with their general graphs and key features.
[link] and [link] summarize the standard features of parabolas with a vertex at a point
| Axis of Symmetry | Equation | Focus | Directrix | Endpoints of Latus Rectum |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?