| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
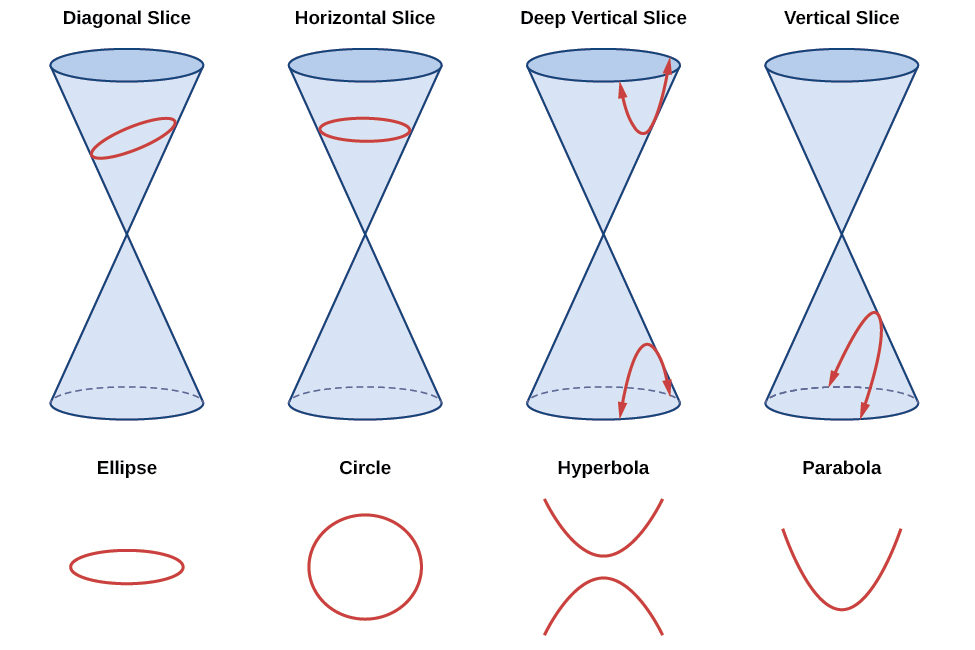
As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions, which we also call a cone . The way in which we slice the cone will determine the type of conic section formed at the intersection. A circle is formed by slicing a cone with a plane perpendicular to the axis of symmetry of the cone. An ellipse is formed by slicing a single cone with a slanted plane not perpendicular to the axis of symmetry. A parabola is formed by slicing the plane through the top or bottom of the double-cone, whereas a hyperbola is formed when the plane slices both the top and bottom of the cone. See [link] .
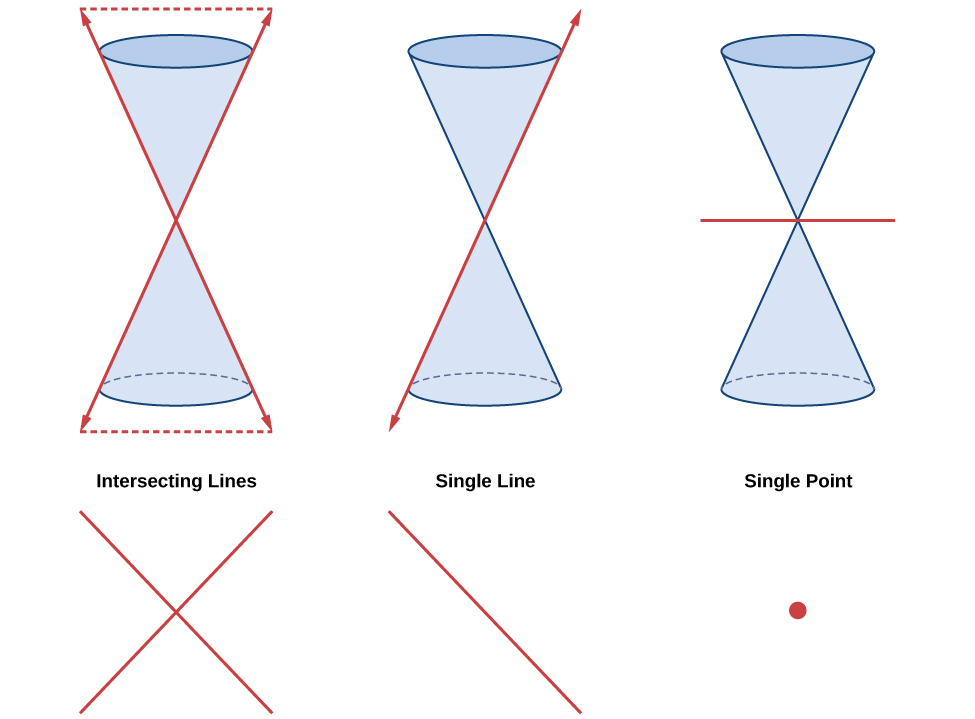
Ellipses, circles, hyperbolas, and parabolas are sometimes called the nondegenerate conic sections , in contrast to the degenerate conic sections , which are shown in [link] . A degenerate conic results when a plane intersects the double cone and passes through the apex. Depending on the angle of the plane, three types of degenerate conic sections are possible: a point, a line, or two intersecting lines.
In previous sections of this chapter, we have focused on the standard form equations for nondegenerate conic sections. In this section, we will shift our focus to the general form equation, which can be used for any conic. The general form is set equal to zero, and the terms and coefficients are given in a particular order, as shown below.
where and are not all zero. We can use the values of the coefficients to identify which type conic is represented by a given equation.
You may notice that the general form equation has an term that we have not seen in any of the standard form equations. As we will discuss later, the term rotates the conic whenever is not equal to zero.
| Conic Sections | Example |
|---|---|
| ellipse | |
| circle | |
| hyperbola | |
| parabola | |
| one line | |
| intersecting lines | |
| parallel lines | |
| a point | |
| no graph |
A conic section has the general form
where and are not all zero.
[link] summarizes the different conic sections where and and are nonzero real numbers. This indicates that the conic has not been rotated.
| ellipse | |
| circle | |
| hyperbola | where and are positive |
| parabola |
Given the equation of a conic, identify the type of conic.
If
B = 0, the conic section will have a vertical and/or horizontal axes. If
B does not equal 0, as shown below, the conic section is rotated.
Notice the phrase “may be” in the definitions. That is because the equation may not represent a conic section at all, depending on the values of
A ,
B ,
C ,
D ,
E , and
F . For example, the degenerate case of a circle or an ellipse is a point:
when
A and
B have the same sign.
The degenerate case of a hyperbola is two intersecting straight lines:
when A and B have opposite signs.
On the other hand, the equation,
when A and B are positive does not represent a graph at all, since there are no real ordered pairs which satisfy it.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?