| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
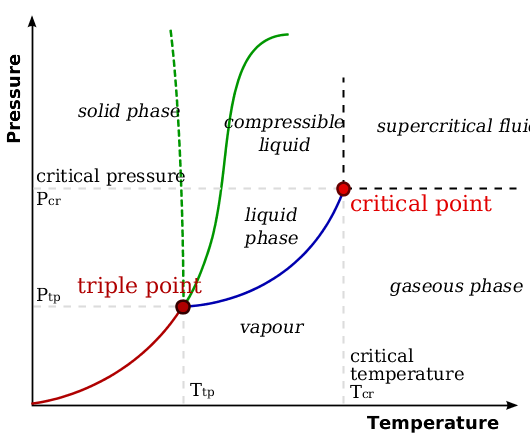
[link] shows the stark differences between two phases in relation to the surrounding conditions. There exist two ambiguous regions. One of these is the point at which all three lines intersect: the triple point. This is the temperature and pressure at which all three states can exist in a dynamic equilibrium. The second ambiguous point comes at the end of the liquid/gas line, where it just ends. At this temperature and pressure, the pure substance has reached a point where it will no longer exist as just one phase or the other: it exists as a hybrid phase – a liquid and gas dynamic equilibrium.
As a result of the dynamic liquid-gas equilibrium, supercritical fluids possess three unique qualities: increased density (on the scale of a liquid), increased diffusivity (similar to that of a gas), and lowered viscosity (on the scale of a gas). [link] shows the similarities in each of these properties. Remember, each of these explains a part of why SFC is an advantageous method of chemical separation.
| Density (g/mL) | Diffusivity (cm 2 /s) | Dynamic viscosity (g/cm s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | 1 x 10 -3 | 1 x 10 -1 | 1 x 10 -2 |
| Liquid | 1.0 | 5 x 10 -6 | 1 x 10 -4 |
| Supercritical fluid | 3 x 10 -1 | 1 x 10 -3 | 1 x 10 -2 |
How are these properties useful? An ideal mobile phase and solvent will do three things well: interact with other particles, carry the sample through the column, and quickly (but accurately) elute it.
Density, as a concept, is simple: the denser something is, the more likely that it will interact with particles it moves through. Affected by an increase in pressure (given constant temperature), density is largely affected by a substance entering the supercritical fluid zone. Supercritical fluids are characterized with densities comparable to those of liquids, meaning they have a better dissolving effect and act as a better carrier gas. High densities among supercritical fluids are imperative for both their effect as solvents and their effect as carrier gases.
Diffusivity refers to how fast the substance can spread among a volume. With increased pressure comes decreased diffusivity (an inverse relationship) but with increased temperature comes increased diffusivity (a direct relationship related to their kinetic energy). Because supercritical fluids have diffusivity values between a gas and liquid, they carry the advantage of a liquid’s density, but the diffusivity closer to that of a gas. Because of this, they can quickly carry and elute a sample, making for an efficient mobile phase.
Finally, dynamic viscosity can be viewed as the resistance to other components flowing through, or intercalating themselves, in the supercritical fluid. Dynamic viscosity is hardly affected by temperature or pressure for liquids, whereas it can be greatly affected for supercritical fluids. With the ability to alter dynamic viscosity through temperature and pressure, the operator can determine how resistant their supercritical fluid should be.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?