| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The sample from previous experiment (TPR) will be used for this experiment. Ultra high-purity argon will be used to purge the sample at a flow rate of 40 cm 3 /min. The sample will be heated to 200 °C in order to remove all chemisorbed hydrogen atoms from the Pd(0) surface. The sample is cooled down to 40 °C. Argon will be used as carrier gas at a flow of 40 cm 3 /min. Filaments temperature will be 175 °C and the detector temperature will be 110 °C. The injection loop has a volume of 0.03610 cm 3 @ STP. As shown in [link] ., hydrogen pulses will be injected in to the flow stream, carried by argon to become in contact and react with the sample. It should be noted that the first pulse of hydrogen was almost completely adsorbed by the sample. The second and third pulses show how the samples is been saturated. The positive value of the TCD detector is consistent with our assumptions. Since hydrogen has a higher thermal conductivity than argon, as it flows through the detector it will tend to cool down the filaments, the detector will then apply a positive voltage to the filaments in order to maintain a constant temperature.
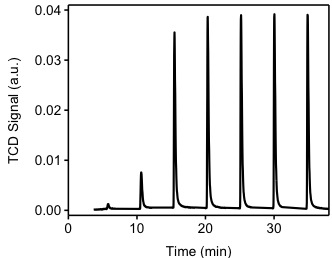
[link] shows the integration of the peaks from [link] . This integration is performed by an automated software provided with the instrument. It should be noted that the first pulse was completely consumed by the sample, the pulse was injected between time 0 and 5 minutes. From [link] we observe that during the first four pulses, hydrogen is consumed by the sample. After the fourth pulse, it appears the sample is not consuming hydrogen. The experiment continues for a total of seven pulses, at this point the software determines that no consumption is occurring and stops the experiment. Pulse eight is denominated the "saturation peak", meaning the pulse at which no hydrogen was consumed.
| Pulse n | Area |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.000471772 |
| 3 | 0.00247767 |
| 4 | 0.009846683 |
| 5 | 0.010348201 |
| 6 | 0.010030243 |
| 7 | 0.009967717 |
| 8 | 0.010580979 |
Using [link] the change in area (Δarea n ) is calculated for each peak pulse area (area n )and compared to that of the saturation pulse area (area saturation = 0.010580979). Each of these changes in area is proportional to an amount of hydrogen consumed by the sample in each pulse. [link] Shows the calculated change in area.
| Pulse n | Area n | ΔArea n |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.010580979 |
| 2 | 0.000471772 | 0.0105338018 |
| 3 | 0.00247767 | 0.008103309 |
| 4 | 0.009846683 | 0.000734296 |
| 5 | 0.010348201 | 0.000232778 |
| 6 | 0.010030243 | 0.000550736 |
| 7 | 0.009967717 | 0.000613262 |
| 8 | 0.010580979 | 0 |
The Δarea n values are then converted into hydrogen gas consumption using [link] , where F c is the area-to-volume conversion factor for hydrogen and SW is the weight of the sample. F c is equal to 2.6465 cm 3 /peak area. [link] shows the results of the volume adsorbed and the cumulative volume adsorbed. Using the data on [link] , a series of calculations can now be performed in order to have a better understanding of our catalyst properties.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?