| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
a = 5.783 + 0.1560 x + 0.0212 x 2
c = 11.628 + 0.3340 x + 0.0277 x 2
The large difference in ionic radii between S and Te (0.37 Å) prevents formation of solid solutions in the CuInS 2-x Te x system, however, the single alloy CuInS 1.5 Te 0.5 has been reported.
Once single crystals of high purity silicon or gallium arsenide are produced they are cut into wafers such that the exposed face of these wafers is either the crystallographic {100} or {111} planes. The relative structure of these surfaces are important with respect to oxidation, etching and thin film growth. These processes are orientation-sensitive; that is, they depend on the direction in which the crystal slice is cut.
The principle planes in a crystal may be differentiated in a number of ways, however, the atom and/or bond density are useful in predicting much of the chemistry of semiconductor surfaces. Since both silicon and gallium arsenide are fcc structures and the {100} and {111} are the only technologically relevant surfaces, discussions will be limited to fcc {100} and {111}.
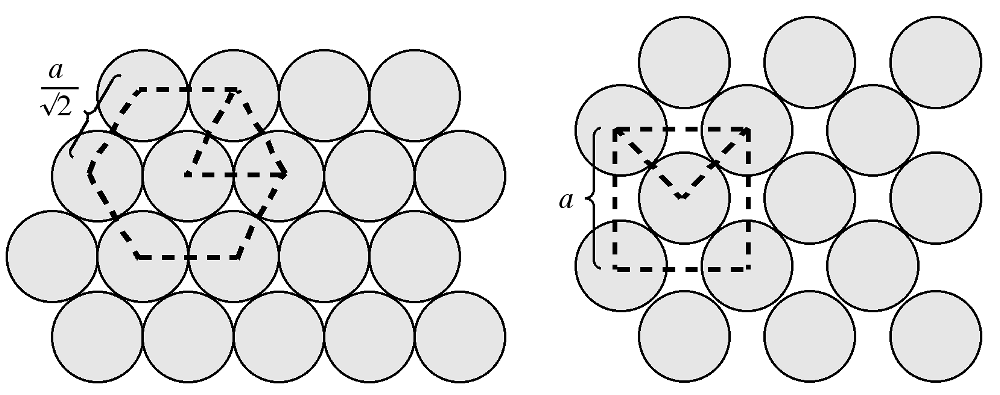
The atom density of a surface may be defined as the number of atoms per unit area. [link] shows a schematic view of the {111} and {100} planes in a fcc lattice. The {111} plane consists of a hexagonal close packed array in which the crystal directions within the plane are oriented at 60° to each other. The hexagonal packing and the orientation of the crystal directions are indicated in [link] b as an overlaid hexagon. Given the intra-planar inter-atomic distance may be defined as a function of the lattice parameter, the area of this hexagon may be readily calculated. For example in the case of silicon, the hexagon has an area of 38.30 Å 2 . The number of atoms within the hexagon is three: the atom in the center plus 1/3 of each of the six atoms at the vertices of the hexagon (each of the atoms at the hexagons vertices is shared by three other adjacent hexagons). Thus, the atom density of the {111} plane is calculated to be 0.0783 Å -2 . Similarly, the atom density of the {100} plane may be calculated. The {100} plane consists of a square array in which the crystal directions within the plane are oriented at 90° to each other. Since the square is coincident with one of the faces of the unit cell the area of the square may be readily calculated. For example in the case of silicon, the square has an area of 29.49 Å 2 . The number of atoms within the square is 2: the atom in the center plus 1/4 of each of the four atoms at the vertices of the square (each of the atoms at the corners of the square are shared by four other adjacent squares). Thus, the atom density of the {100} plane is calculated to be 0.0678 Å -2 . While these values for the atom density are specific for silicon, their ratio is constant for all diamond cubic and zinc blende structures: {100}:{111} = 1:1.155. In general, the fewer dangling bonds the more stable a surface structure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?