| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Because of its widespread use in SFC, it’s important to discuss what makes CO 2 an ideal supercritical fluid. One of the biggest limitations to most mobile phases in SFC is getting them to reach the critical point. This means extremely high temperatures and pressures, which is not easily attainable. The best gases for this are ones that can achieve a critical point at relatively low temperatures and pressures.
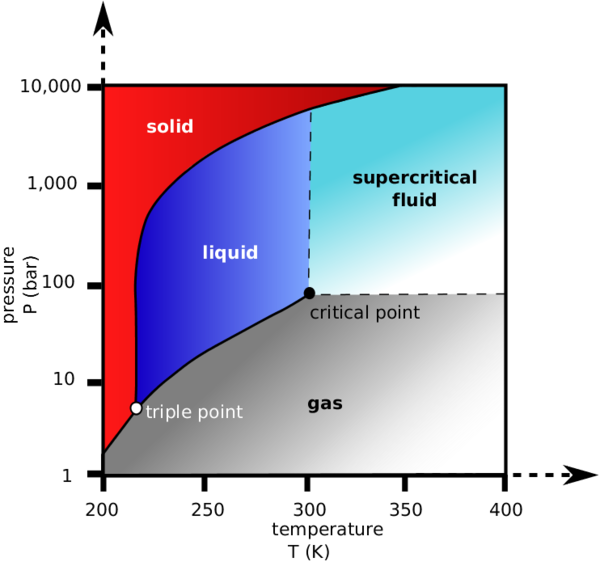
As seen from [link] , CO 2 has a critical temperature of approximately 31 °C and a critical pressure of around 73 atm. These are both relatively low numbers and are thus ideal for SFC. Of course, with every upside there exists a downside. In this case, CO 2 lacks polarity, which makes it difficult to use its mobile phase properties to elute polar samples. This is readily fixed with a modifier, which will be discussed later.
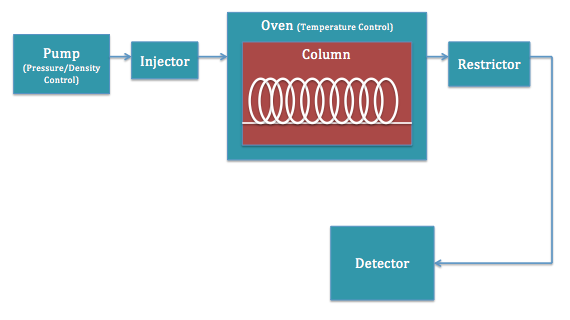
SFC has a similar instrument setup to most other chromatography machines, notably HPLC. The functions of the parts are very similar, but it is important to understand them for the purposes of understanding the technique. [link] shows a schematic representation of a typical apparatus.
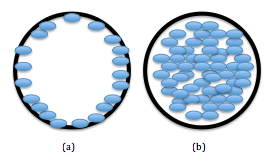
There are two main types of columns used with SFC: open tubular and packed, as seen below. The columns themselves are near identical to HPLC columns in terms of material and coatings. Open tubular columns are most used and are coated with a cross-linked silica material (powdered quartz, SiO 2 ) for a stationary phase. Column lengths range, but usually fall between 10 and 20 meters and are coated with less than 1 µm of silica stationary phase. [link] demonstrates the differences in the packing of the two columns.
Injectors act as the main site for the insertion of samples. There are many different kinds of injectors that depend on a multitude of factors. For packed columns, the sample must be small and the exact amount depends on the column diameter. For open tubular columns, larger volumes can be used. In both cases, there are specific injectors that are used depending on how the sample needs to be placed in the instrument. A loop injector is used mainly for preliminary testing. The sample is fed into a chamber that is then flushed with the supercritical fluid and pushed down the column. It uses a low-pressure pump before proceeding with the full elution at higher pressures. An inline injector allows for easy control of sample volume. A high-pressure pump forces the (specifically measured) sample into a stream of eluent, which proceeds to carry the sample through the column. This method allows for specific dilutions and greater flexibility. For samples requiring no dilution or immediate interaction with the eluent, an in-column injector is useful. This allows the sample to be transferred directly into the packed column and the mobile phase to then pass through the column.
The existence of a supercritical fluid, as discussed previously, depends on high temperatures and high pressures. The pump is responsible for delivering the high pressures. By pressurizing the gas (or liquid), it can cause the substance to become dense enough to exhibit signs of the desired supercritical fluid. Because pressure couples with heat to create the supercritical fluid, the two are usually very close together on the instrument.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?