| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
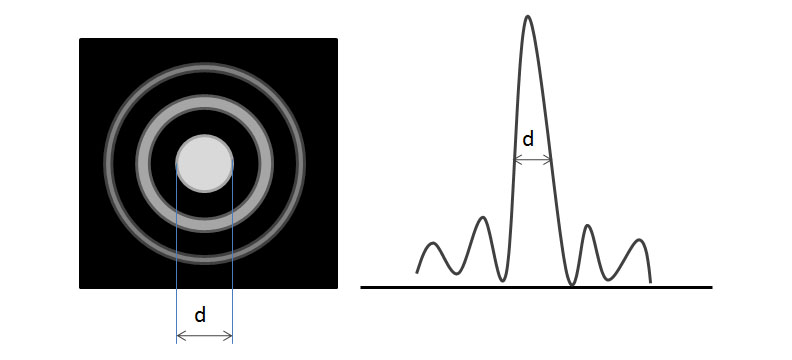
Aberrations distort the image and we try to minimize the effect as much as possible. Chromatic aberrations are caused by the multiple wavelengths present in white light. Spherical aberrations are formed by focusing inside and outside the ideal focal length and caused by the imperfections within the objective lenses. Astigmatism is because of further distortions in the lens. All aberrations decrease the overall resolution of the microscope.
Electrons are charged particles and can interact with air molecules therefore the SEM and TEM instruments require extremely high vacuum to obtain images (10 -7 atm). High vacuum ensures that very few air molecules are in the electron beam column. If the electron beam interacts with an air molecule, the air will become ionized and damage the beam filament, which is very costly to repair. The charge of the electron allows scanning and also inherently has a very small deflection angle off the source of the beam.
The electrons are generated with a thermionic filament. A tungsten (W) or LaB 6 filament is chosen based on the needs of the user. LaB 6 is much more expensive and tungsten filaments meet the needs of the average user. The microscope can be operated as field emission (tungsten filament).
To accurately interpret electron microscopy images, the user must be familiar with how high energy electrons can interact with the sample and how these interactions affect the image. The probability that a particular electron will be scattered in a certain way is either described by the cross section, σ, or mean free path, λ, which is the average distance which an electron travels before being scattered.
Elastic scatter, or Rutherford scattering, is defined as a process which deflects an electron but does not decrease its energy. The wavelength of the scattered electron can be detected and is proportional to the atomic number. Elastically scattered electrons have significantly more energy that other types and provide mass contrast imaging. The mean free path, λ, is larger for smaller atoms meaning that the electron travels farther.
Any process that causes the incoming electron to lose a detectable amount of energy is considered inelastic scattering. The two most common types of inelastic scatter are phonon scattering and plasmon scattering. Phonon scattering occurs when a primary electron looses energy by exciting a phonon, atomic vibrations in a solid, and heats the sample a small amount. A Plasmon is an oscillation within the bulk electrons in the conduction band for metals. Plasmon scattering occurs when an electron interacts with the sample and produces plasmons, which typically have 5 - 30 eV energy loss and small λ.
A secondary effect is a term describing any event which may be detected outside the specimen and is essentially how images are formed. To form an image, the electron must interact with the sample in one of the aforementioned ways and escape from the sample and be detected. Secondary electrons (SE) are the most common electrons used for imaging due to high abundance and are defined, rather arbitrarily, as electrons with less than 50 eV energy after exiting the sample. Backscattered electrons (BSE) leave the sample quickly and retain a high amount of energy; however there is a much lower yield of BSE. Backscattered electrons are used in many different imaging modes. Refer to [link] for a diagram of interaction depths corresponding to various electron interactions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?