| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
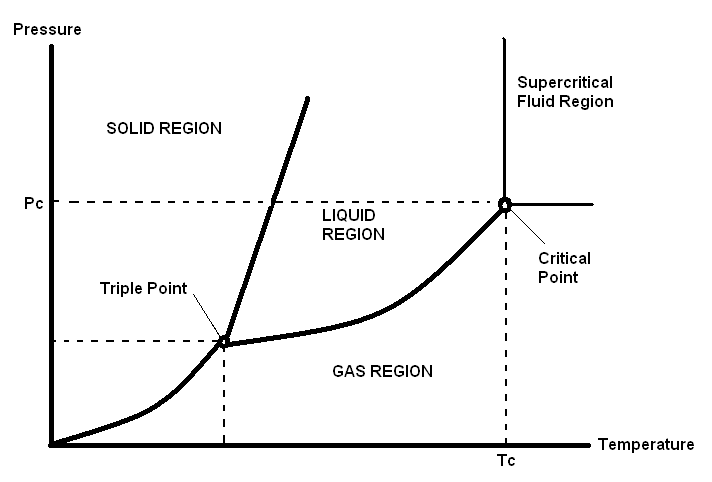
There is another characteristic point in the phase diagram, the critical point (CP). This point is obtained at critical temperature ( T c ) and critical pressure ( P c ). After the CP, no matter how much pressure or temperature is increased, the material cannot transform from gas to liquid or from liquid to gas phase. This form is the supercritical fluid form. Increasing temperature cannot result in turning to gas, and increasing pressure cannot result in turning to liquid at this point. In the phase diagram, the field above T c and P c values is defined as the supercritical region.
In theory, the supercritical region can be reached in two ways:
The critical point is characteristic for each material, resulting from the characteristic T c and P c values for each substance.
As mentioned above, SF shares some common features with both gases and liquids. This enables us to take advantage of a correct combination of the properties.
Density characteristic of a supercritical fluid is between that of a gas and a liquid, but closer to that of a liquid. In the supercritical region, density of a supercritical fluid increases with increased pressure (at constant temperature). When pressure is constant, density of the material decreases with increasing temperature. The dissolving effect of a supercritical fluid is dependent on its density value. Supercritical fluids are also better carriers than gases thanks to their higher density. Therefore, density is an essential parameter for analytical techniques using supercritical fluids as solvents.
Diffusivity of a supercritical fluid can be 100 x that of a liquid and 1 / 1,000 to 1 / 10,000 x less than a gas. Because supercritical fluids have more diffusivity than a liquid, it stands to reason a solute can show better diffusivity in a supercritical fluid than in a liquid. Diffusivity is parallel with temperature and contrary with pressure. Increasing pressure affects supercritical fluid molecules to become closer to each other and decreases diffusivity in the material. The greater diffusivity gives supercritical fluids the chance to be faster carriers for analytical applications. Hence, supercritical fluids play an important role for chromatography and extraction methods.
Viscosity for a supercritical fluid is almost the same as a gas, being approximately 1 / 10 of that of a liquid. Thus, supercritical fluids are less resistant than liquids towards components flowing through. The viscosity of supercritical fluids is also distinguished from that of liquids in that temperature has a little effect on liquid viscosity, where it can dramatically influence supercritical fluid viscosity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?