| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is a chromatographic method that separate the molecules in the solutions based on the size (hydrodynamic volume). This column is often used for the separation of macromolecules and of macromolecules from small molecules. After the analyte is injected into the column, molecules smaller than he pore size of the stationary phase enter the porous particles during the separation and flow through he intricate channels of the stationary phase. Thus smaller components have a longer path to traverse and elute from the column later than the larger ones. Since the molecular volume is related to molecular weight, it is expected that retention volume will depend to some degree on the molecular weight of the polymeric materials. The relation between the retention time and the molecular weight is shown in [link] .
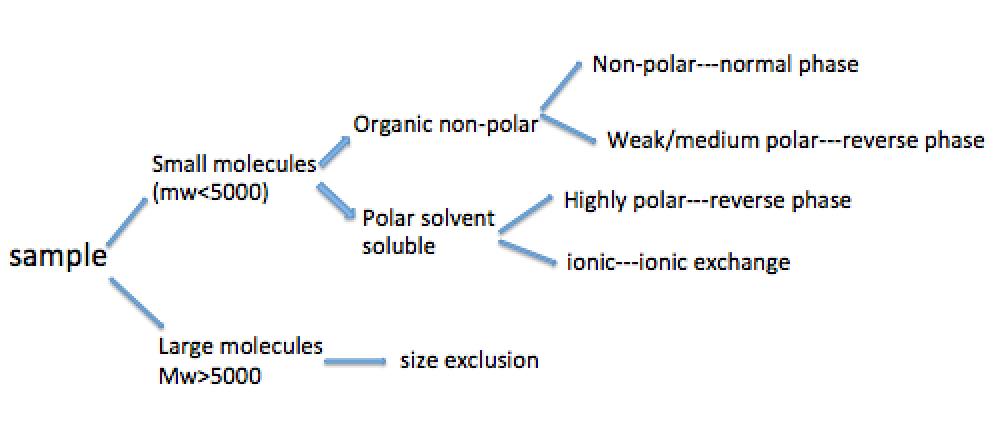
Usually the type of HPLC separation method to use depends on the chemical nature and physicochemical parameters of the samples. [link] shows a flow chart of preliminary selection for the separation method according to the properties of the analyte.
Detectors that are commonly used for liquid chromatography include ultraviolet-visible absorbance detectors, refractive index detectors, fluorescence detectors, and mass spectrometry. Regardless of the class, a LC detector should ideally have the characteristics of about 10 -12 -10 -11 g/mL, and a linear dynamic range of five or six orders. The principal characteristics of the detectors to be evaluated include dynamic range, response index or linearity, linear dynamic range, detector response, detector sensitivity, etc.
Among these detectors, the most economical and popular methods are UV and refractive index (RI) detectors. They have rather broad selectivity reasonable detection limits most of the time. The RI detector was the first detector available for commercial use. This method is particularly useful in the HPLC separation according to size, and the measurement is directly proportional to the concentration of polymer and practically independent of the molecular weight. The sensitivity of RI is 10 -6 g/mL, the linear dynamic range is from 10 -6 to 10 -4 g/mL, and the response index is between 0.97 and 1.03.
UV detectors respond only to those substances that absorb UV light at the wavelength of the source light. A great many compounds absorb light in the UV range (180-350 nm) including substances having one or more double bonds and substances having unshared electrons. and the relationship between the intensity of UV light transmitted through the cell and solute concentration is given by Beer’s law, [link] and [link] .
Where I 0 is the intensity of the light entering the cell, and I T is the light transmitted through the cell, l is the path length of the cell, c is the concentration of the solute, and k is the molar absorption coefficient of the solute. UV detectors include fixed wavelength UV detector and multi wavelength UV detector. The fixed wavelength UV detector has sensitivity of 5*10 -8 g/mL, has linear dynamic range between 5*10 -8 and 5* 10-4 g/mL, and the response index is between 0.98 and 1.02. The multi-wavelength UV detector has sensitivity of 10 -7 g/mL, the linear dynamic range is between 5*10 -7 and 5*10 -4 g/mL, and the response index is from 0.97 to 1.03. UV detectors could be used effectively for the reverse-phase separations and ion exchange chromatography. UV detectors have high sensitivity, are economically affordable, and easy to operate. Thus UV detector is the most common choice of detector for HPLC.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?