| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Accordingly, atomic coordinates are usually expressed in terms of fractional coordinates, (x, y, z). This coordinate system is coincident with the cell axes ( a , b , c ) and relates to the position of the atom in terms of the fraction along each axis. Consider the atom in the cubic cell discussion above. The atom was 1.5 Å in the a direction away from the origin. As the a axis is 3.52 Å long, the atom is ( 1.5 / 3.52 ) or 0.43 of the axis away from the origin. Similarly, it is ( 2.1 / 3.52 ) or 0.60 of the b axis and ( 2.4 / 3.5 ) or 0.68 of the c axis. The fractional coordinates of this atom are, therefore, (0.43, 0.60, 0.68). The coordinates of the equivalent atom in the next cell over in the a direction, however, are easily calculated as this atom is simply 1 unit cell away in a . Thus, all one has to do is add 1 to the x coordinate: (1.43, 0.60, 0.68). Such transformations can be performed regardless of the shape of the unit cell. Fractional coordinates, therefore, are used to retain and manipulate crystal information.
The designation of the individual vectors within any given crystal lattice is accomplished by the use of whole number multipliers of the lattice parameter of the point at which the vector exits the unit cell. The vector is indicated by the notation [ hkl ], where h , k , and l are reciprocals of the point at which the vector exits the unit cell. The origination of all vectors is assumed defined as [000]. For example, the direction along the a -axis according to this scheme would be [100] because this has a component only in the a -direction and no component along either the b or c axial direction. A vector diagonally along the face defined by the a and b axis would be [110], while going from one corner of the unit cell to the opposite corner would be in the [111]direction. [link] shows some examples of the various directions in the unit cell. The crystal direction notation is made up of the lowest combination of integers and represents unit distances rather than actual distances. A [222] direction is identical to a [111], so [111] is used. Fractions are not used. For example, a vector that intercepts the center of the top face of the unit cell has the coordinates x = 1/2, y = 1/2, z = 1. All have to be inversed to convert to the lowest combination of integers (whole numbers); i.e., [221]in [link] . Finally, all parallel vectors have the same crystal direction, e.g., the four vertical edges of the cell shown in [link] all have the crystal direction [ hkl ] = [001].
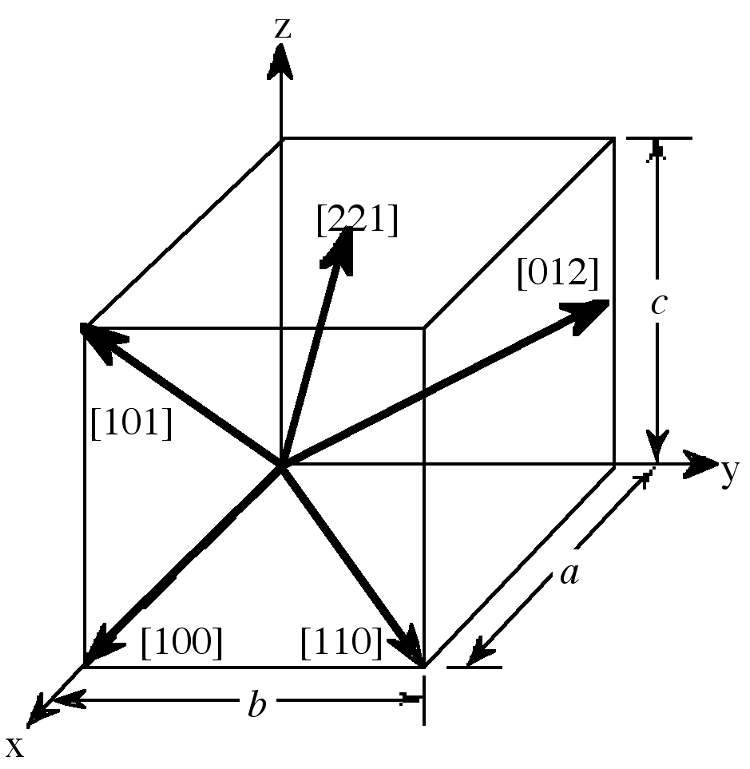
Crystal directions may be grouped in families. To avoid confusion there exists a convention in the choice of brackets surrounding the three numbers to differentiate a crystal direction from a family of direction. For a direction, square brackets [ hkl ] are used to indicate an individual direction. Angle brackets< hkl >indicate a family of directions. A family of directions includes any directions that are equivalent in length and types of atoms encountered. For example, in a cubic lattice, the [100], [010], and [001] directions all belong to the<100>family of planes because they are equivalent. If the cubic lattice were rotated 90°, the a , b , and c directions would remain indistinguishable, and there would be no way of telling on which crystallographic positions the atoms are situated, so the family of directions is the same. In a hexagonal crystal, however, this is not the case, so the [100] and [010]would both be<100>directions, but the [001] direction would be distinct. Finally, negative directions are identified with a bar over the negative number instead of a minus sign.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?