| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Modifiers are added to the mobile phase to play with its properties. As mentioned a few times previously, CO 2 supercritical fluid lacks polarity. In order to add polarity to the fluid (without causing reactivity), a polar modifier will often be added. Modifiers usually raise the critical pressure and temperature of the mobile phase a little, but in return add polarity to the phase and result in a fully resolved sample. Unfortunately, with too much modifier, higher temperatures and pressures are needed and reactivity increases (which is dangerous and bad for the operator). Modifiers, such as ethanol or methanol, are used in small amounts as needed for the mobile phase in order to create a more polar fluid.
Clearly, SFC possesses some extraordinary potential as far as chromatography techniques go. It has some incredible capabilities that allow efficient and accurate resolution of mixtures. Below is a summary of its advantages and disadvantages stacked against other conventional (competing) chromatography methods.
While the use of SFC has been mainly organic-oriented, there are still a few ways that inorganic compound mixtures are separated using the method. The two main ones, separation of chiral compounds (mainly metal-ligand complexes) and organometallics are discussed here.
For chiral molecules, the procedures and choice of column in SFC are very similar to those used in HPLC. Packed with cellulose type chiral stationary phase (or some other chiral stationary phase), the sample flows through the chiral compound and only molecules with a matching chirality will stick to the column. By running a pure CO 2 supercritical fluid mobile phase, the non-sticking enantiomer will elute first, followed eventually (but slowly) with the other one.
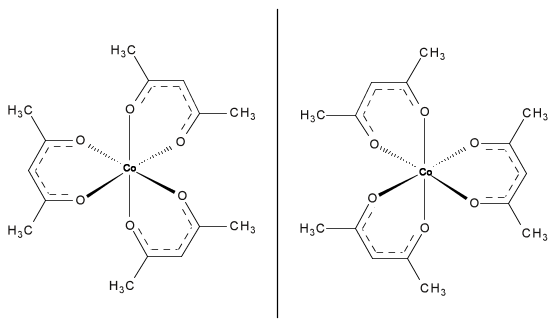
In the field of inorganic chemistry, a racemic mixture of Co(acac) 3 , both isomers shown in [link] , has been resolved using a cellulose-based chiral stationary phase. The SFC method was one of the best and most efficient instruments in analyzing the chiral compound. While SFC easily separates coordinate covalent compounds, it is not necessary to use such an extensive instrument to separate mixtures of it since there are many simpler techniques.
Many d-block organometallics are highly reactive and easily decompose in air. SFC offers a way to chromatograph mixtures of large, unusual organometallic compounds. Large cobalt and rhodium based organometallic compound mixtures have been separated using SFC ( [link] ) without exposing the compounds to air.
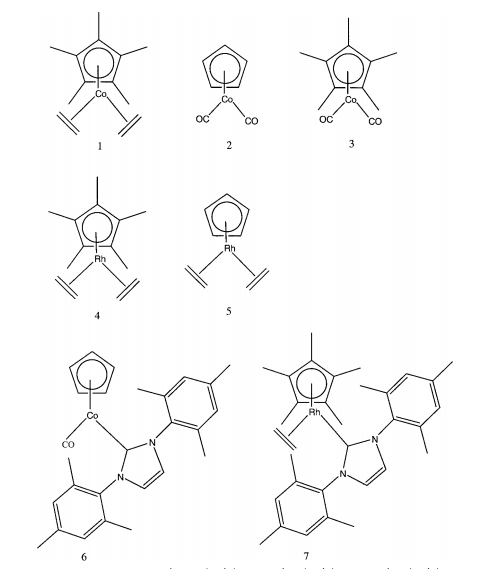
By using a stationary phase of siloxanes, oxygen-linked silicon particles with different substituents attached, the organometallics were resolved based on size and charge. Thanks to the non-polar, highly diffusive, and high viscosity properties of a 100% CO 2 supercritical fluid, the mixture was resolved and analyzed with a flame ionization detector. It was determined that the method was sensitive enough to detect impurities of 1%. Because the efficiency of SFC is so impressive, the potential for it in the organometallic field is huge. Identifying impurities down to 1% shows promise for not only preliminary data in experiments, but quality control as well.
While it may have its drawbacks, SFC remains an untapped resource in the ways of chromatography. The advantages to using supercritical fluids as mobile phases demonstrate how resolution can be increased without sacrificing time or increasing column length. Nonetheless, it is still a well-utilized resource in the organic, biomedical, and pharmaceutical industries. SFC shows promise as a reliable way of separating and analyzing mixtures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?