| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Melting point (Mp) is a quick and easy analysis that may be used to qualitatively identify relatively pure samples (approximately<10% impurities). It is also possible to use this analysis to quantitatively determine purity. Melting point analysis, as the name suggests, characterizes the melting point, a stable physical property, of a sample in a straightforward manner, which can then be used to identify the sample.
Although different designs of apparatus exist, they all have some sort of heating or heat transfer medium with a control, a thermometer, and often a backlight and magnifying lens to assist in observing melting ( [link] ). Most models today utilize capillary tubes containing the sample submerged in a heated oil bath. The sample is viewed with a simple magnifying lens. Some new models have digital thermometers and controls and even allow for programming. Programming allows more precise control over the starting temperature, ending temperature and the rate of change of the temperature.
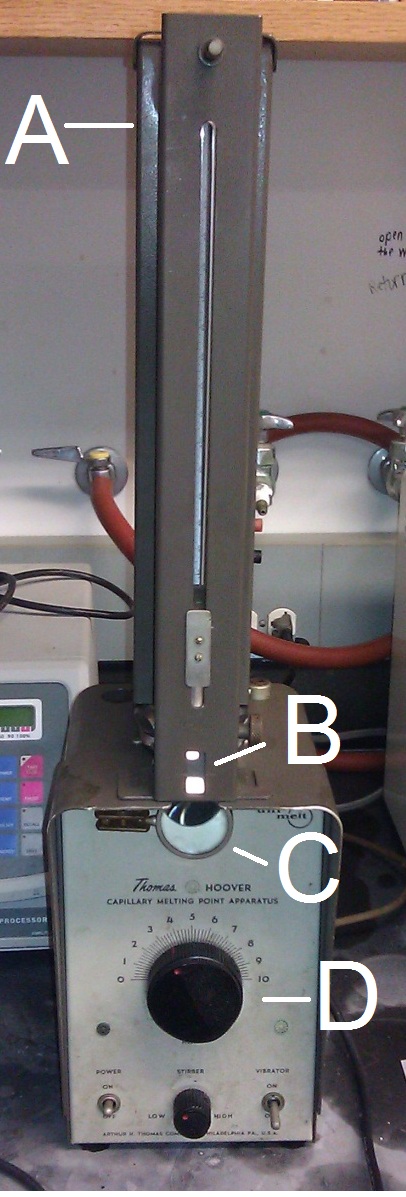
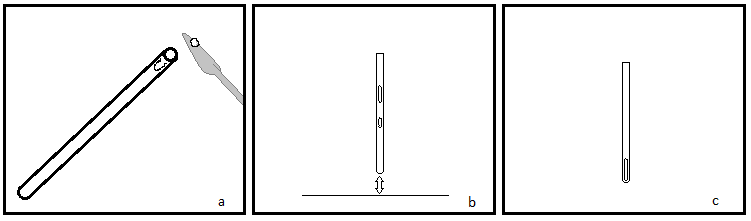
For melting point analysis, preparation is straight forward. The sample must be thoroughly dried and relatively pure (<10% impurities). The dry sample should then be packed into a melting point analysis capillary tube, which is simply a glass capillary tube with only one open end. Only 1 to 3 mm of sample is needed for sufficient analysis. The sample needs to be packed down into the closed end of the tube. This may be done by gently tapping the tube or dropping it upright onto a hard surface ( [link] ). Some apparatuses have a vibrator to assist in packing the sample. Finally the tube should be placed into the machine. Some models can accommodate multiple samples.
Performing analysis is different from machine to machine, but the overall process is the same ( [link] ). If possible, choose a starting temperature, ending temperature, and rate of change of temperature. If the identity of the sample is known, base the starting and ending temperatures from the known melting point of the chemical, providing margins on both sides of the range. If using a model without programming, simply turn on the machine and monitor the rate of temperature change manually.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?