| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) is one of the most commonly employed surface analysis techniques. It uses the energy of emitted electrons to identify the elements present in a sample, similar to X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The main difference is that XPS uses an X-ray beam to eject an electron while AES uses an electron beam to eject an electron. In AES, the sample depth is dependent on the escape energy of the electrons. It is not a function of the excitation source as in XPS. In AES, the collection depth is limited to 1-5 nm due to the small escape depth of electrons, which permits analysis of the first 2 - 10 atomic layers. In addition, a typical analysis spot size is roughly 10 nm. A representative AES spectrum illustrating the number of emitted electrons, N, as a function of kinetic energy, E, in direct form (red) and in differentiated form (black) is shown in [link] .
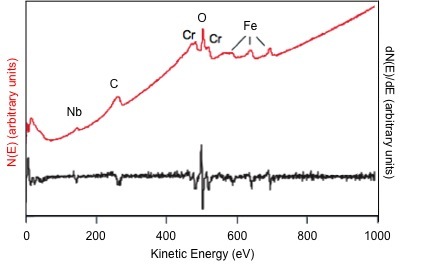
Like XPS, AES measures the kinetic energy (E k ) of an electron to determine its binding energy (E b ). The binding energy is inversely proportional to the kinetic energy and can be found from [link] , where hν is the energy of the incident photon and ΔΦ is the difference in work function between the sample and the detector material.
Since the E b is dependent on the element and the electronic environment of the nucleus, AES can be used to distinguish elements and their oxidation states. For instance, the energy required to remove an electron from Fe 3+ is more than in Fe 0 . Therefore, the Fe 3+ peak will have a lower E k than the Fe 0 peak, effectively distinguishing the oxidation states.
An Auger electron comes from a cascade of events. First, an electron beam comes in with sufficient energy to eject a core electron creating a vacancy (see [link] A). Typical energies of the primary electrons range from 3 - 30 keV. A secondary electron (imaging electron) of higher energy drops down to fill the vacancy (see [link] B) and emits sufficient energy to eject a tertiary electron (Auger electron) from a higher shell (see [link] C).
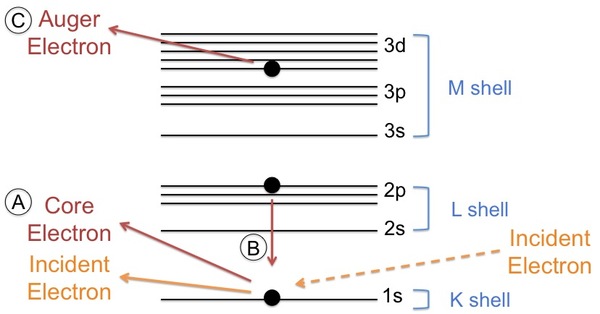
The shells from which the electrons move from lowest to highest energy are described as the K shell, L shell, and M shell. This nomenclature is related to quantum numbers. Explicitly, the K shell represents the 1s orbital, the L shell represents the 2s and 2p orbitals, and the M shell represents the 3s, 3p, and 3d orbitals. The cascade of events typically begins with the ionization of a K shell electron, followed by the movement of an L shell electron into the K shell vacancy. Then, either an L shell electron or M shell electron is ejected. It depends on the element, which peak is prevalent but often both peaks will be present. The peak seen in the spectrum is labeled according to the shells involved in the movement of the electrons. For example, an electron ejected from a gold atom could be labeled as Au KLL or Au KLM.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?