| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
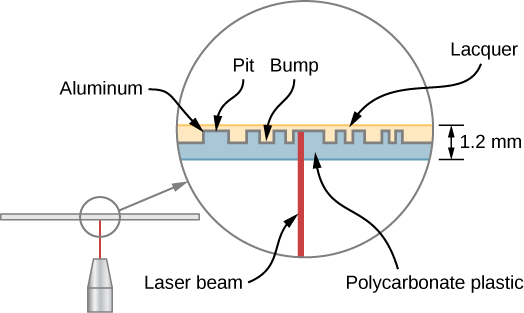
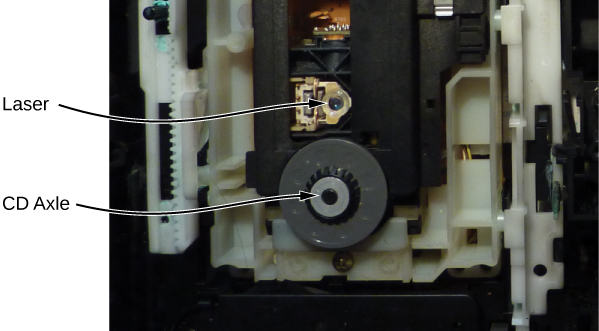
A CD player uses a laser to read this digital information. Laser light is suited to this purpose, because coherent light can be focused onto an incredibly small spot and therefore distinguish between bumps and pits in the CD. After processing by player components (including a diffraction grating, polarizer, and collimator), laser light is focused by a lens onto the CD surface. Light that strikes a bump (“land”) is merely reflected, but light that strikes a “pit” destructively interferes, so no light returns (the details of this process are not important to this discussion). Reflected light is interpreted as a “1” and unreflected light is interpreted as a “0.” The resulting digital signal is converted into an analog signal, and the analog signal is fed into an amplifier that powers a device such as a pair of headphones. The laser system of a CD player is shown in [link] .
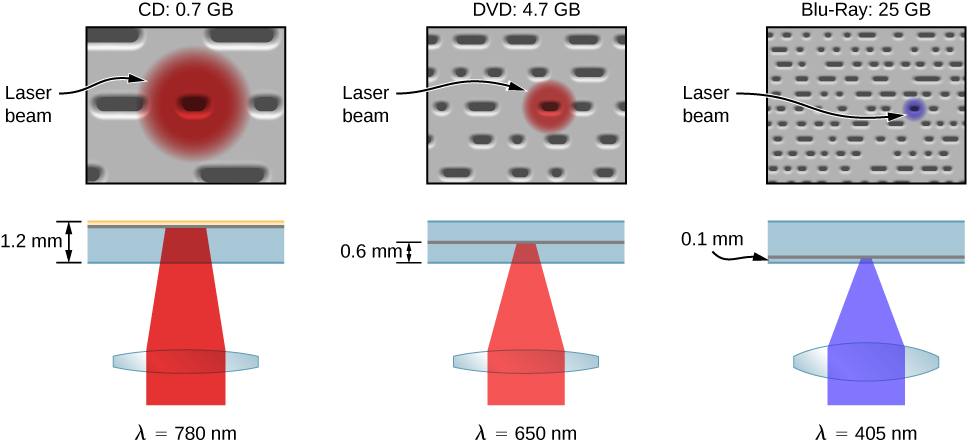
Like a CD player, a Blu-Ray player reads digital information (video or audio) stored on a disc, and a laser is used to record this information. The pits on a Blu-Ray disc are much smaller and more closely packed together than for a CD, so much more information can be stored. As a result, the resolving power of the laser must be greater. This is achieved using short wavelength blue laser light—hence, the name “Blu-” Ray. (CDs and DVDs use red laser light.) The different pit sizes and player-hardware configurations of a CD, DVD, and Blu-Ray player are shown in [link] . The pit sizes of a Blu-Ray disk are more than twice as small as the pits on a DVD or CD. Unlike a CD, a Blu-Ray disc store data on a polycarbonate layer, which places the data closer to the lens and avoids readability problems. A hard coating is used to protect the data since it is so close to the surface.
| Orbital angular momentum | |
| z -component of orbital angular momentum | |
| Radial probability density function | |
| Spin angular momentum | |
| z -component of spin angular momentum | |
| Electron spin magnetic moment | |
| Electron orbital magnetic dipole moment | |
| Potential energy associated with the magnetic
interaction between the orbital magnetic dipole moment and an external magnetic field |
|
| Maximum number of electrons in a subshell of
a hydrogen atom |
|
| Selection rule for atomic transitions in a
hydrogen-like atom |
|
| Moseley’s law for X-ray production |
Distinguish between coherent and monochromatic light.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?