| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An extended object such as the container in [link] can be treated as a collection of points, and we can apply the method above to locate the image of each point on the extended object, thus forming the extended image.
If an object is situated in front of two mirrors, you may see images in both mirrors. In addition, the image in the first mirror may act as an object for the second mirror, so the second mirror may form an image of the image. If the mirrors are placed parallel to each other and the object is placed at a point other than the midpoint between them, then this process of image-of-an-image continues without end, as you may have noticed when standing in a hallway with mirrors on each side. This is shown in [link] , which shows three images produced by the blue object. Notice that each reflection reverses front and back, just like pulling a right-hand glove inside out produces a left-hand glove (this is why a reflection of your right hand is a left hand). Thus, the fronts and backs of images 1 and 2 are both inverted with respect to the object, and the front and back of image 3 is inverted with respect to image 2, which is the object for image 3.
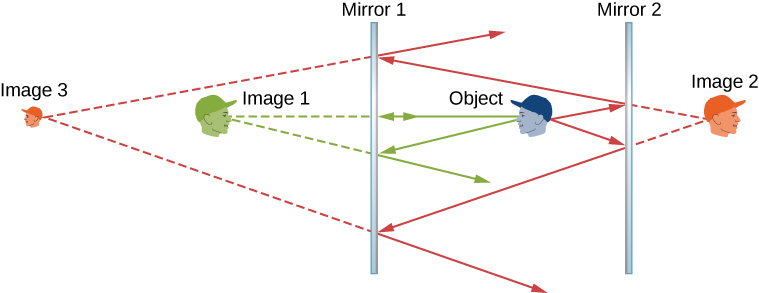
You may have noticed that image 3 is smaller than the object, whereas images 1 and 2 are the same size as the object. The ratio of the image height with respect to the object height is called magnification . More will be said about magnification in the next section.
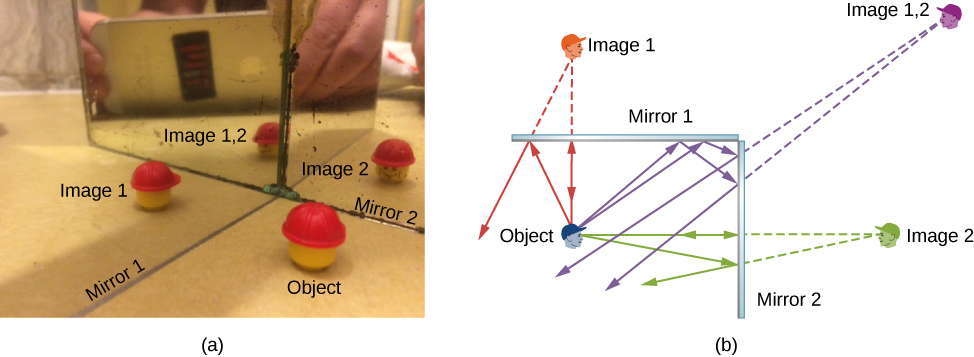
Infinite reflections may terminate. For instance, two mirrors at right angles form three images, as shown in part (a) of [link] . Images 1 and 2 result from rays that reflect from only a single mirror, but image 1,2 is formed by rays that reflect from both mirrors. This is shown in the ray-tracing diagram in part (b) of [link] . To find image 1,2, you have to look behind the corner of the two mirrors.
What are the differences between real and virtual images? How can you tell (by looking) whether an image formed by a single lens or mirror is real or virtual?
Virtual image cannot be projected on a screen. You cannot distinguish a real image from a virtual image simply by judging from the image perceived with your eye.
Can you see a virtual image? Explain your response.
Can you photograph a virtual image?
Yes, you can photograph a virtual image. For example, if you photograph your reflection from a plane mirror, you get a photograph of a virtual image. The camera focuses the light that enters its lens to form an image; whether the source of the light is a real object or a reflection from mirror (i.e., a virtual image) does not matter.
Can you project a virtual image onto a screen?
Is it necessary to project a real image onto a screen to see it?
No, you can see the real image the same way you can see the virtual image. The retina of your eye effectively serves as a screen.
Devise an arrangement of mirrors allowing you to see the back of your head. What is the minimum number of mirrors needed for this task?
If you wish to see your entire body in a flat mirror (from head to toe), how tall should the mirror be? Does its size depend upon your distance away from the mirror? Provide a sketch.
The mirror should be half your size and its top edge should be at the level of your eyes. The size does not depend on your distance from the mirror.
Consider a pair of flat mirrors that are positioned so that they form an angle of 120 . An object is placed on the bisector between the mirrors. Construct a ray diagram as in [link] to show how many images are formed.
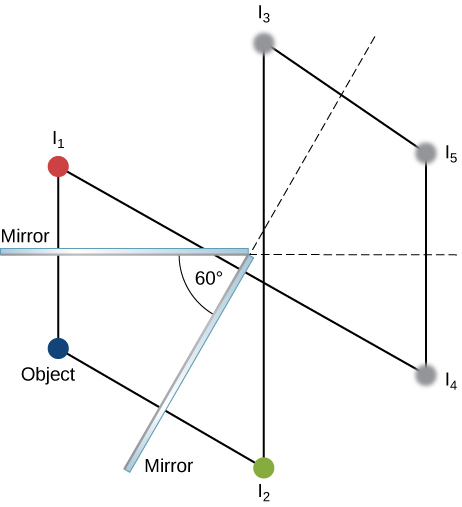
Consider a pair of flat mirrors that are positioned so that they form an angle of 60 . An object is placed on the bisector between the mirrors. Construct a ray diagram as in [link] to show how many images are formed.
By using more than one flat mirror, construct a ray diagram showing how to create an inverted image.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?