| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
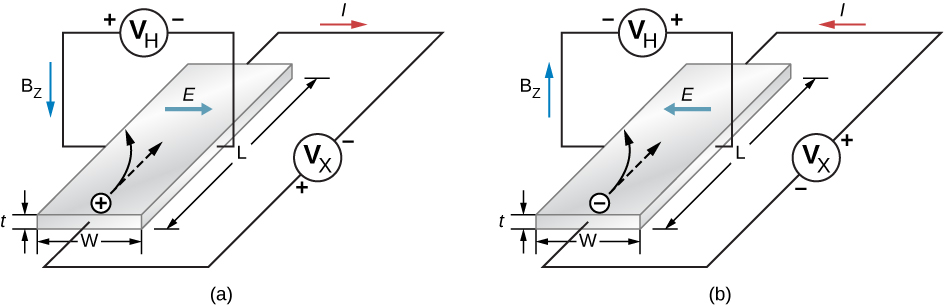
where is the Hall voltage; v is the hole’s drift velocity , or average velocity of a particle that moves in a partially random fashion; B is the magnetic field strength; and w is the width of the strip. Note that the Hall voltage is transverse to the voltage that initially produces current through the material. A measurement of the sign of this voltage (or potential difference) confirms the collection of holes on the top side of the strip. The magnitude of the Hall voltage yields the drift velocity ( v ) of the majority carriers.
Additional information can also be extracted from the Hall voltage. Note that the electron current density (the amount of current per unit cross-sectional area of the semiconductor strip) is
where q is the magnitude of the charge, n is the number of charge carriers per unit volume, and v is the drift velocity. The current density is easily determined by dividing the total current by the cross-sectional area of the strip, q is charge of the hole (the magnitude of the charge of a single electron), and u is determined by the Hall effect [link] . Hence, the above expression for the electron current density gives the number of charge carriers per unit volume, n . A similar analysis can be conducted for negatively charged carriers in an n -type material (see [link] ).
What kind of semiconductor is produced if germanium is doped with (a) arsenic, and (b) gallium?
a. Germanium has four valence electrons. If germanium doped with arsenic (five valence electrons), four are used in bonding and one electron will be left for conduction. This produces an n -type material. b. If germanium is doped with gallium (three valence electrons), all three electrons are used in bonding, leaving one hole for conduction. This results in a p -type material.
What kind of semiconductor is produced if silicon is doped with (a) phosphorus, and (b) indium?
What is the Hall effect and what is it used for?
The Hall effect is the production of a potential difference due to motion of a conductor through an external magnetic field. This effect can be used to determine the drift velocity of the charge carriers (electrons or hole). If the current density is measured, this effect can also determine the number of charge carriers per unit volume.
For an n -type semiconductor, how do impurity atoms alter the energy structure of the solid?
For a p -type semiconductor, how do impurity atoms alter the energy structure of the solid?
It produces new unfilled energy levels just above the filled valence band. These levels accept electrons from the valence band.
An experiment is performed to demonstrate the Hall effect. A thin rectangular strip of semiconductor with width 10 cm and length 30 cm is attached to a battery and immersed in a 1.50- T field perpendicular to its surface. This produced a Hall voltage of 12 V. What is the drift velocity of the charge carriers?
Suppose that the cross-sectional area of the strip (the area of the face perpendicular to the electric current) presented to the in the preceding problem is and the current is independently measured to be 2 mA. What is the number density of the charge carriers?
A current-carrying copper wire with cross-section has a drift velocity of 0.02 cm/s. Find the total current running through the wire.
The Hall effect is demonstrated in the laboratory. A thin rectangular strip of semiconductor with width 5 cm and cross-sectional area is attached to a battery and immersed in a field perpendicular to its surface. The Hall voltage reads 12.5 V and the measured drift velocity is 50 m/s. What is the magnetic field?
5 T

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?