| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
These two maxima actually correspond to values of slightly less than rad and rad. Since the total length of the arc of the phasor diagram is always the radius of the arc decreases as increases. As a result, and turn out to be slightly larger for arcs that have not quite curled through rad and rad, respectively. The exact values of for the maxima are investigated in [link] . In solving that problem, you will find that they are less than, but very close to,
To calculate the intensity at an arbitrary point P on the screen, we return to the phasor diagram of [link] . Since the arc subtends an angle at the center of the circle,
and
where E is the amplitude of the resultant field. Solving the second equation for E and then substituting r from the first equation, we find
Now defining
we obtain
This equation relates the amplitude of the resultant field at any point in the diffraction pattern to the amplitude at the central maximum. The intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude, so
where is the intensity at the center of the pattern.
For the central maximum, , is also zero and we see from l’Hôpital’s rule that so that For the next maximum, rad, we have rad and when substituted into [link] , it yields
in agreement with what we found earlier in this section using the diameters and circumferences of phasor diagrams. Substituting rad into [link] yields a similar result for .
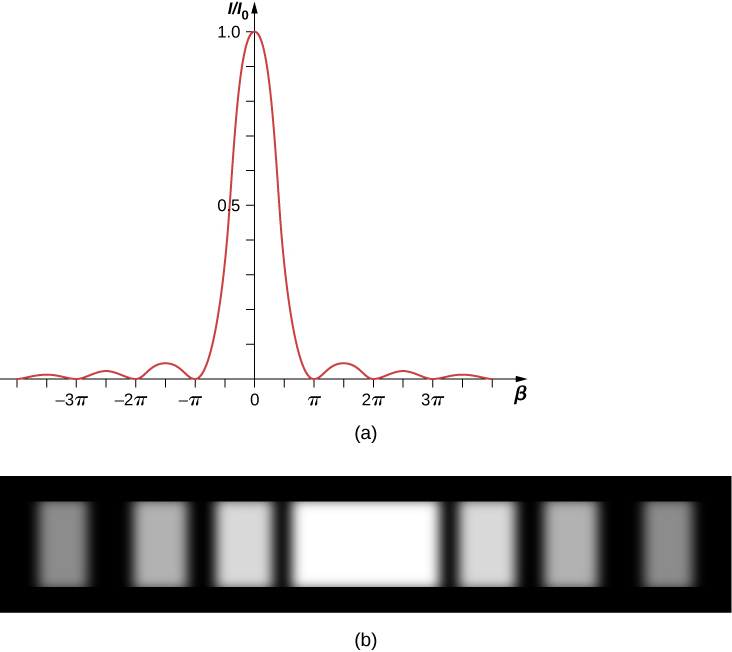
A plot of [link] is shown in [link] and directly below it is a photograph of an actual diffraction pattern. Notice that the central peak is much brighter than the others, and that the zeros of the pattern are located at those points where which occurs when rad. This corresponds to
or
which is [link] .
[link] gives
From [link] , we can calculate
Check Your Understanding For the experiment in [link] , at what angle from the center is the third maximum and what is its intensity relative to the central maximum?
,
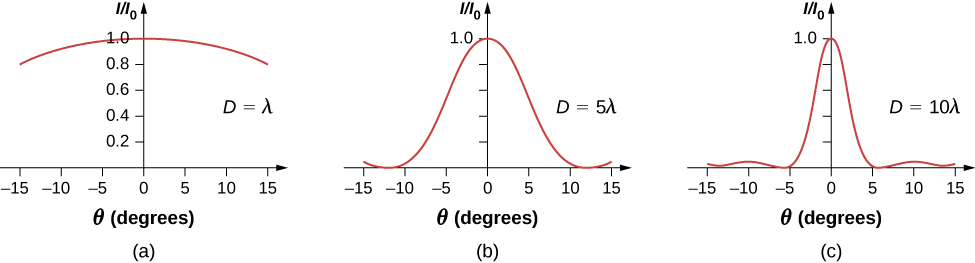
If the slit width D is varied, the intensity distribution changes, as illustrated in [link] . The central peak is distributed over the region from to . For small , this corresponds to an angular width Hence, an increase in the slit width results in a decrease in the width of the central peak . For a slit with the central peak is very sharp, whereas if , it becomes quite broad.
A diffraction experiment in optics can require a lot of preparation but this simulation by Andrew Duffy offers not only a quick set up but also the ability to change the slit width instantly. Run the simulation and select “Single slit.” You can adjust the slit width and see the effect on the diffraction pattern on a screen and as a graph.
In [link] , the parameter looks like an angle but is not an angle that you can measure with a protractor in the physical world. Explain what represents.
The parameter is the arc angle shown in the phasor diagram in [link] . The phase difference between the first and last Huygens wavelet across the single slit is and is related to the curvature of the arc that forms the resultant phasor that determines the light intensity.
A single slit of width is illuminated by a sodium yellow light of wavelength 589 nm. Find the intensity at a angle to the axis in terms of the intensity of the central maximum.
A single slit of width 0.1 mm is illuminated by a mercury light of wavelength 576 nm. Find the intensity at a angle to the axis in terms of the intensity of the central maximum.
The width of the central peak in a single-slit diffraction pattern is 5.0 mm. The wavelength of the light is 600 nm, and the screen is 2.0 m from the slit. (a) What is the width of the slit? (b) Determine the ratio of the intensity at 4.5 mm from the center of the pattern to the intensity at the center.
Consider the single-slit diffraction pattern for , , and . Find the intensity in terms of at , , , , and .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?