| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
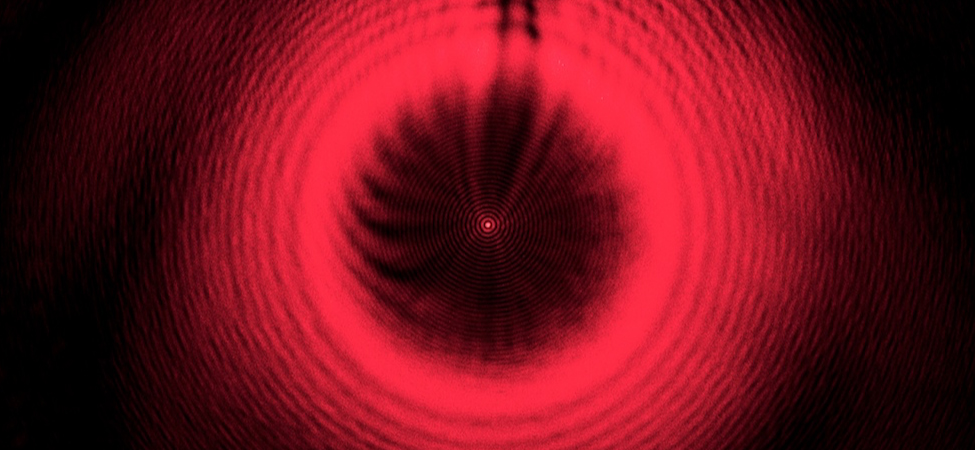
Imagine passing a monochromatic light beam through a narrow opening—a slit just a little wider than the wavelength of the light. Instead of a simple shadow of the slit on the screen, you will see that an interference pattern appears, even though there is only one slit.
In the chapter on interference, we saw that you need two sources of waves for interference to occur. How can there be an interference pattern when we have only one slit? In The Nature of Light , we learned that, due to Huygens’s principle, we can imagine a wave front as equivalent to infinitely many point sources of waves. Thus, a wave from a slit can behave not as one wave but as an infinite number of point sources. These waves can interfere with each other, resulting in an interference pattern without the presence of a second slit. This phenomenon is called diffraction .
Another way to view this is to recognize that a slit has a small but finite width. In the preceding chapter, we implicitly regarded slits as objects with positions but no size. The widths of the slits were considered negligible. When the slits have finite widths, each point along the opening can be considered a point source of light—a foundation of Huygens’s principle. Because real-world optical instruments must have finite apertures (otherwise, no light can enter), diffraction plays a major role in the way we interpret the output of these optical instruments. For example, diffraction places limits on our ability to resolve images or objects. This is a problem that we will study later in this chapter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?