| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The energy of radiation detected by a radio-signal receiving antenna comes as the energy of an electromagnetic wave. The same energy of radiation detected by a photocurrent in the photoelectric effect comes as the energy of individual photon particles. Therefore, the question arises about the nature of electromagnetic radiation: Is a photon a wave or is it a particle? Similar questions may be asked about other known forms of energy. For example, an electron that forms part of an electric current in a circuit behaves like a particle moving in unison with other electrons inside the conductor. The same electron behaves as a wave when it passes through a solid crystalline structure and forms a diffraction image. Is an electron a wave or is it a particle? The same question can be extended to all particles of matter—elementary particles, as well as compound molecules—asking about their true physical nature. At our present state of knowledge, such questions about the true nature of things do not have conclusive answers. All we can say is that wave-particle duality exists in nature: Under some experimental conditions, a particle appears to act as a particle, and under different experimental conditions, a particle appears to act a wave. Conversely, under some physical circumstances electromagnetic radiation acts as a wave, and under other physical circumstances, radiation acts as a beam of photons.
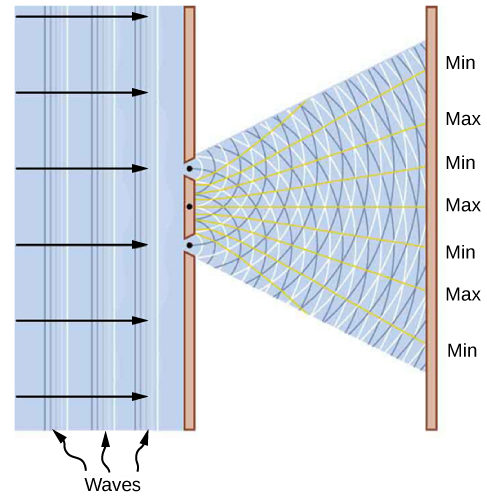
This dualistic interpretation is not a new physics concept brought about by specific discoveries in the twentieth century. It was already present in a debate between Isaac Newton and Christiaan Huygens about the nature of light, beginning in the year 1670. According to Newton, a beam of light is a collection of corpuscles of light. According to Huygens, light is a wave. The corpuscular hypothesis failed in 1803, when Thomas Young announced his double-slit interference experiment with light (see [link] ), which firmly established light as a wave. In James Clerk Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism (completed by the year 1873), light is an electromagnetic wave. Maxwell’s classical view of radiation as an electromagnetic wave is still valid today; however, it is unable to explain blackbody radiation and the photoelectric effect, where light acts as a beam of photons.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?