| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
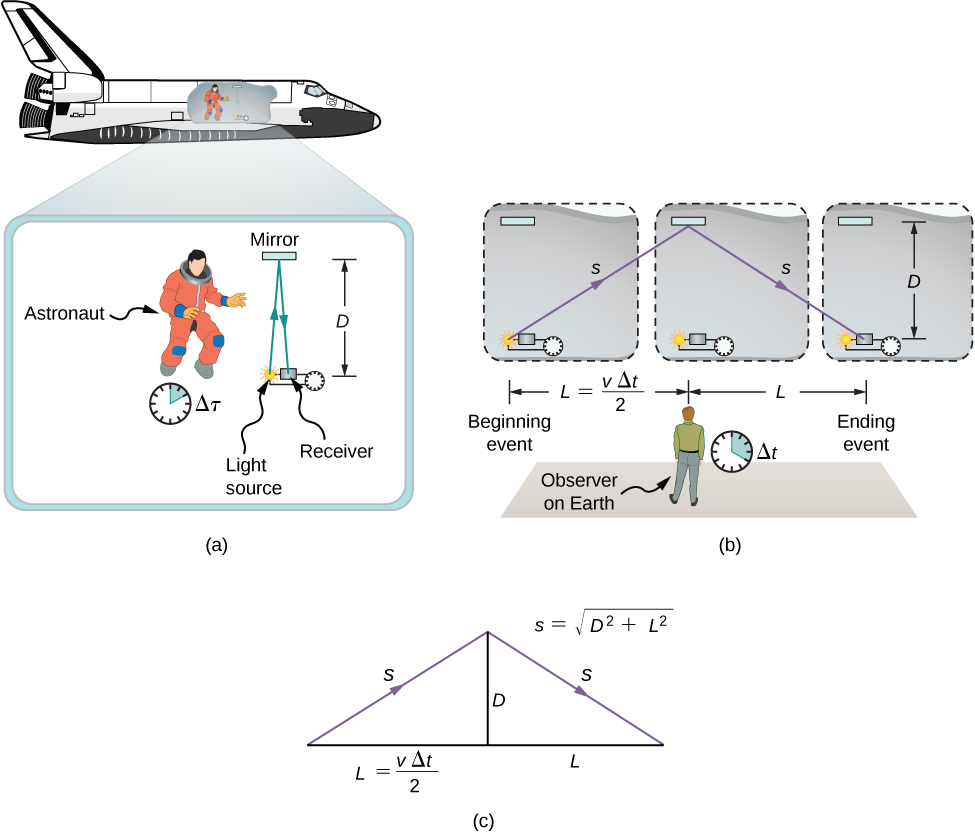
The analysis of simultaneity shows that Einstein’s postulates imply an important effect: Time intervals have different values when measured in different inertial frames. Suppose, for example, an astronaut measures the time it takes for a pulse of light to travel a distance perpendicular to the direction of his ship’s motion (relative to an earthbound observer), bounce off a mirror, and return ( [link] ). How does the elapsed time that the astronaut measures in the spacecraft compare with the elapsed time that an earthbound observer measures by observing what is happening in the spacecraft?
Examining this question leads to a profound result. The elapsed time for a process depends on which observer is measuring it. In this case, the time measured by the astronaut (within the spaceship where the astronaut is at rest) is smaller than the time measured by the earthbound observer (to whom the astronaut is moving). The time elapsed for the same process is different for the observers, because the distance the light pulse travels in the astronaut’s frame is smaller than in the earthbound frame, as seen in [link] . Light travels at the same speed in each frame, so it takes more time to travel the greater distance in the earthbound frame.
Time dilation is the lengthening of the time interval between two events for an observer in an inertial frame that is moving with respect to the rest frame of the events (in which the events occur at the same location).
To quantitatively compare the time measurements in the two inertial frames, we can relate the distances in [link] to each other, then express each distance in terms of the time of travel (respectively either or ) of the pulse in the corresponding reference frame. The resulting equation can then be solved for in terms of
The lengths D and L in [link] are the sides of a right triangle with hypotenuse s . From the Pythagorean theorem,
The lengths 2 s and 2 L are, respectively, the distances that the pulse of light and the spacecraft travel in time in the earthbound observer’s frame. The length D is the distance that the light pulse travels in time in the astronaut’s frame. This gives us three equations:
Note that we used Einstein’s second postulate by taking the speed of light to be c in both inertial frames. We substitute these results into the previous expression from the Pythagorean theorem:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?