| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Analyzing the interference of light passing through two slits lays out the theoretical framework of interference and gives us a historical insight into Thomas Young’s experiments. However, most modern-day applications of slit interference use not just two slits but many, approaching infinity for practical purposes. The key optical element is called a diffraction grating, an important tool in optical analysis.
The analysis of multi-slit interference in Interference allows us to consider what happens when the number of slits N approaches infinity. Recall that secondary maxima appear between the principal maxima. We can see there will be an infinite number of secondary maxima that appear, and an infinite number of dark fringes between them. This makes the spacing between the fringes, and therefore the width of the maxima, infinitesimally small. Furthermore, because the intensity of the secondary maxima is proportional to , it approaches zero so that the secondary maxima are no longer seen. What remains are only the principal maxima, now very bright and very narrow ( [link] ).
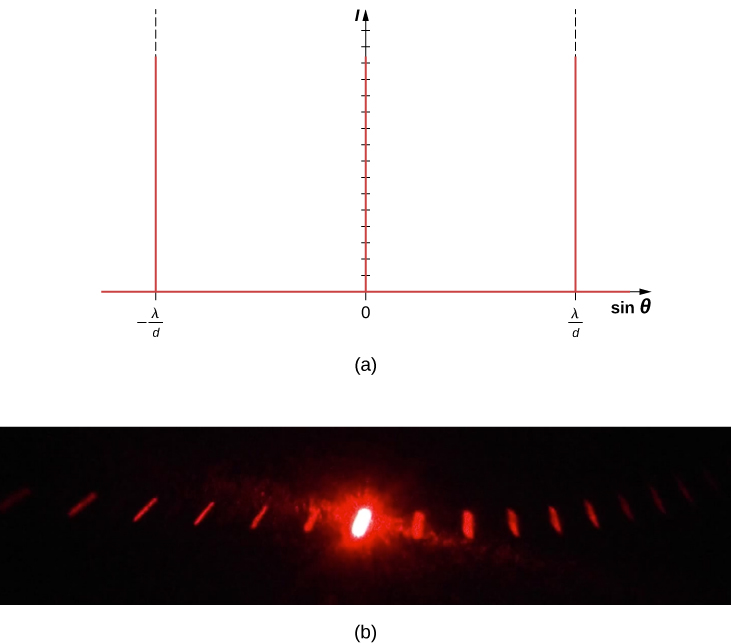
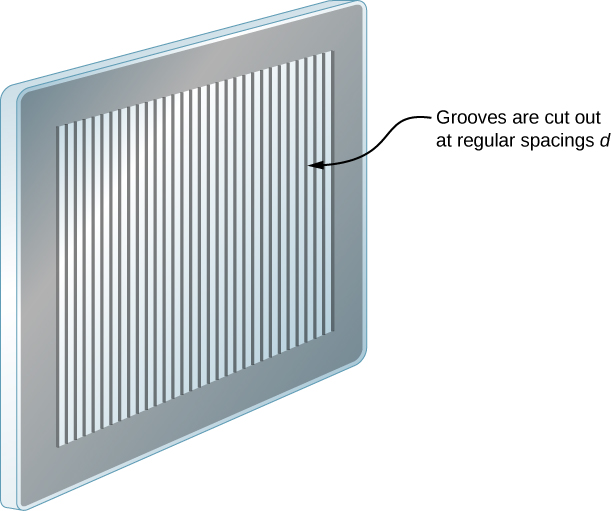
In reality, the number of slits is not infinite, but it can be very large—large enough to produce the equivalent effect. A prime example is an optical element called a diffraction grating . A diffraction grating can be manufactured by carving glass with a sharp tool in a large number of precisely positioned parallel lines, with untouched regions acting like slits ( [link] ). This type of grating can be photographically mass produced rather cheaply. Because there can be over 1000 lines per millimeter across the grating, when a section as small as a few millimeters is illuminated by an incoming ray, the number of illuminated slits is effectively infinite, providing for very sharp principal maxima.
Diffraction gratings work both for transmission of light, as in [link] , and for reflection of light, as on butterfly wings and the Australian opal in [link] . Natural diffraction gratings also occur in the feathers of certain birds such as the hummingbird. Tiny, finger-like structures in regular patterns act as reflection gratings, producing constructive interference that gives the feathers colors not solely due to their pigmentation. This is called iridescence .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?