| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
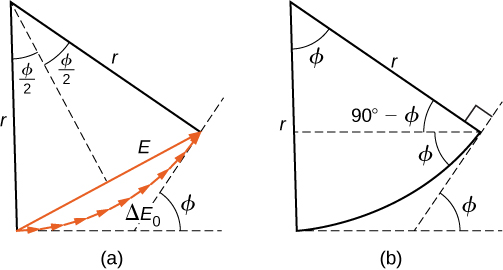
To calculate the intensity of the diffraction pattern, we follow the phasor method used for calculations with ac circuits in Alternating-Current Circuits . If we consider that there are N Huygens sources across the slit shown in [link] , with each source separated by a distance D/N from its adjacent neighbors, the path difference between waves from adjacent sources reaching the arbitrary point P on the screen is This distance is equivalent to a phase difference of The phasor diagram for the waves arriving at the point whose angular position is is shown in [link] . The amplitude of the phasor for each Huygens wavelet is the amplitude of the resultant phasor is E , and the phase difference between the wavelets from the first and the last sources is
With , the phasor diagram approaches a circular arc of length and radius r . Since the length of the arc is for any , the radius r of the arc must decrease as increases (or equivalently, as the phasors form tighter spirals).
The phasor diagram for (the center of the diffraction pattern) is shown in [link] (a) using . In this case, the phasors are laid end to end in a straight line of length the radius r goes to infinity, and the resultant has its maximum value The intensity of the light can be obtained using the relation from Electromagnetic Waves . The intensity of the maximum is then
where . The phasor diagrams for the first two zeros of the diffraction pattern are shown in parts (b) and (d) of the figure. In both cases, the phasors add to zero, after rotating through rad for and rad for .
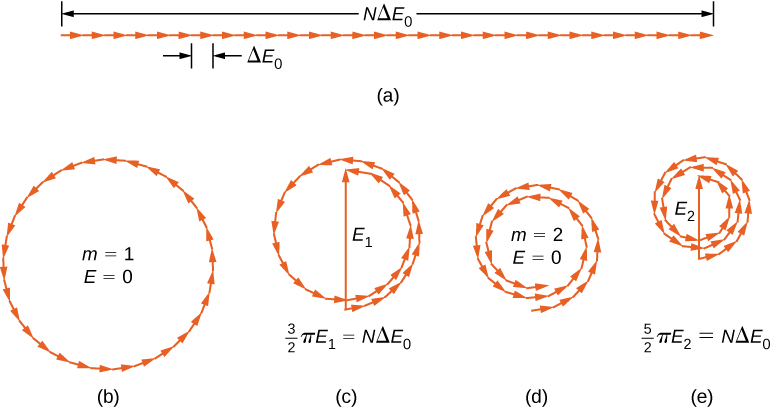
The next two maxima beyond the central maxima are represented by the phasor diagrams of parts (c) and (e). In part (c), the phasors have rotated through rad and have formed a resultant phasor of magnitude . The length of the arc formed by the phasors is Since this corresponds to 1.5 rotations around a circle of diameter , we have
so
and
where
In part (e), the phasors have rotated through rad, corresponding to 2.5 rotations around a circle of diameter and arc length This results in . The proof is left as an exercise for the student ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?