| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
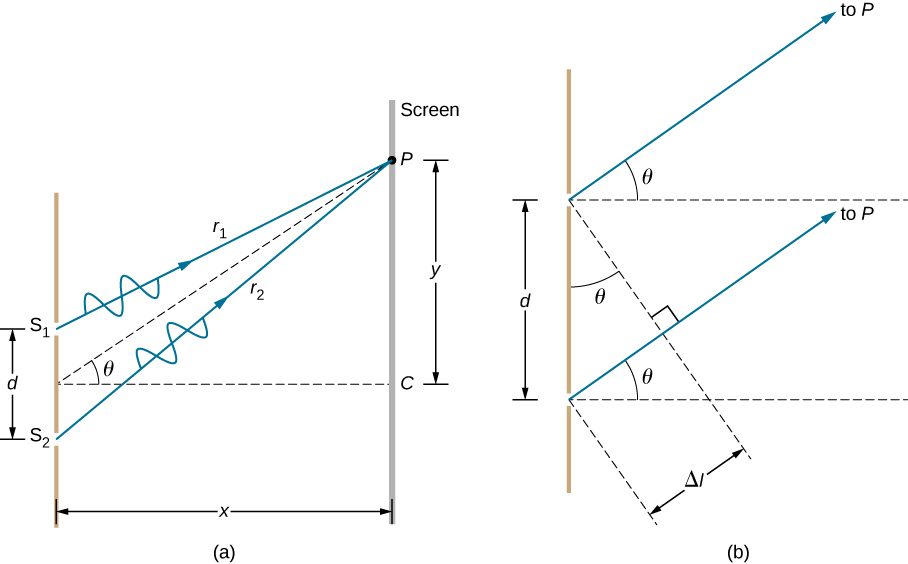
[link] (a) shows how to determine the path length difference for waves traveling from two slits to a common point on a screen. If the screen is a large distance away compared with the distance between the slits, then the angle between the path and a line from the slits to the screen [part (b)] is nearly the same for each path. In other words, and are essentially parallel. The lengths of and differ by , as indicated by the two dashed lines in the figure. Simple trigonometry shows
where d is the distance between the slits. Combining this result with [link] , we obtain constructive interference for a double slit when the path length difference is an integral multiple of the wavelength, or
Similarly, to obtain destructive interference for a double slit, the path length difference must be a half-integral multiple of the wavelength, or
where is the wavelength of the light, d is the distance between slits, and is the angle from the original direction of the beam as discussed above. We call m the order of the interference. For example, is fourth-order interference.
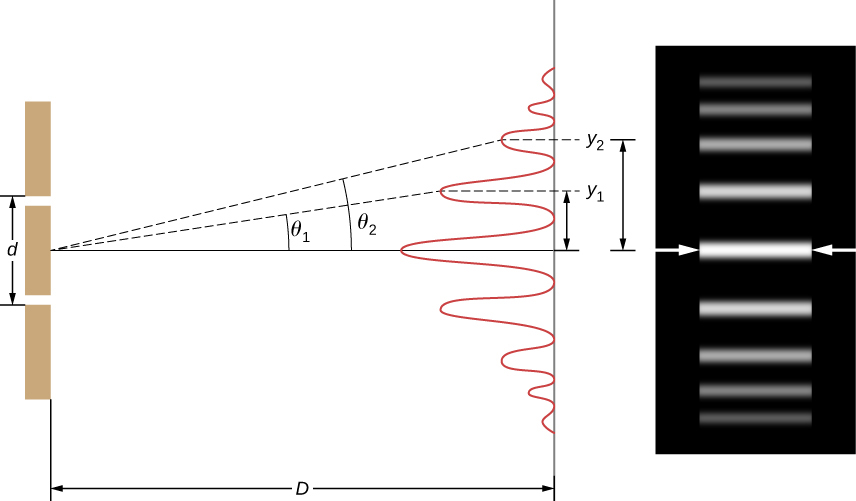
The equations for double-slit interference imply that a series of bright and dark lines are formed. For vertical slits, the light spreads out horizontally on either side of the incident beam into a pattern called interference fringes ( [link] ). The closer the slits are, the more the bright fringes spread apart. We can see this by examining the equation
. For fixed and m , the smaller d is, the larger must be, since . This is consistent with our contention that wave effects are most noticeable when the object the wave encounters (here, slits a distance d apart) is small. Small d gives large , hence, a large effect.
Referring back to part (a) of the figure, is typically small enough that , where is the distance from the central maximum to the m th bright fringe and D is the distance between the slit and the screen. [link] may then be written as
or
Substituting known values yields

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?