| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When rays of light propagate from one medium to another, these rays undergo refraction, which is when light waves are bent at the interface between two media. The refracting surface can form an image in a similar fashion to a reflecting surface, except that the law of refraction (Snell’s law) is at the heart of the process instead of the law of reflection.
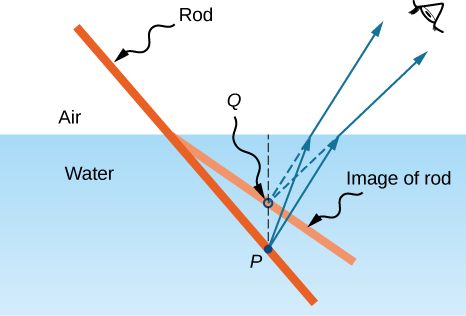
If you look at a straight rod partially submerged in water, it appears to bend at the surface ( [link] ). The reason behind this curious effect is that the image of the rod inside the water forms a little closer to the surface than the actual position of the rod, so it does not line up with the part of the rod that is above the water. The same phenomenon explains why a fish in water appears to be closer to the surface than it actually is.
To study image formation as a result of refraction, consider the following questions:
To be concrete, we consider a simple system consisting of two media separated by a plane interface ( [link] ). The object is in one medium and the observer is in the other. For instance, when you look at a fish from above the water surface, the fish is in medium 1 (the water) with refractive index 1.33, and your eye is in medium 2 (the air) with refractive index 1.00, and the surface of the water is the interface. The depth that you “see” is the image height and is called the apparent depth . The actual depth of the fish is the object height .
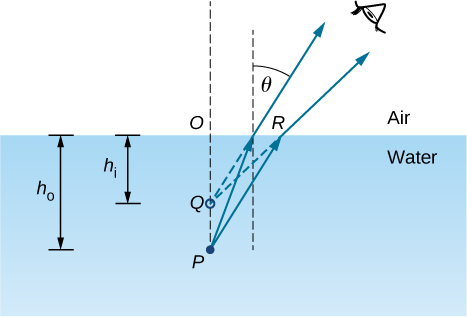
The apparent depth depends on the angle at which you view the image. For a view from above (the so-called “normal” view), we can approximate the refraction angle to be small, and replace sin in Snell’s law by tan . With this approximation, you can use the triangles and to show that the apparent depth is given by
The derivation of this result is left as an exercise. Thus, a fish appears at 3/4 of the real depth when viewed from above.
Spherical shapes play an important role in optics primarily because high-quality spherical shapes are far easier to manufacture than other curved surfaces. To study refraction at a single spherical surface, we assume that the medium with the spherical surface at one end continues indefinitely (a “semi-infinite” medium).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?