| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have been discussing elementary particles, which are some of the smallest things we can study. Now we are going to examine what we know about the universe, which is the biggest thing we can study. The link between these two topics is high energy: The study of particle interactions requires very high energies, and the highest energies we know about existed during the early evolution of the universe. Some physicists think that the unified force theories we described in the preceding section may actually have governed the behavior of the universe in its earliest moments.
In 1929, Edwin Hubble published one of the most important discoveries in modern astronomy. Hubble discovered that (1) galaxies appear to move away from Earth and (2) the velocity of recession ( v ) is proportional to the distance ( d ) of the galaxy from Earth. Both v and d can be determined using stellar light spectra. A best fit to the sample illustrative data is given in [link] . (Hubble’s original plot had a considerable scatter but a general trend was still evident.)
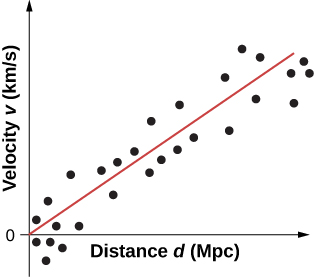
The trend in the data suggests the simple proportional relationship:
where is known as Hubble’s constant . ( Note: 1 Mpc is one megaparsec or one million parsecs, where one parsec is 3.26 light-years.) This relationship, called Hubble’s law , states that distant stars and galaxies recede away from us at a speed of 70 km/s for every one megaparsec of distance from us. Hubble’s constant corresponds to the slope of the line in [link] . Hubble’s constant is a bit of a misnomer, because it varies with time. The value given here is only its value today .
Watch this video to learn more about the history of Hubble’s constant.
Hubble’s law describes an average behavior of all but the closest galaxies. For example, a galaxy 100 Mpc away (as determined by its size and brightness) typically moves away from us at a speed of
This speed may vary due to interactions with neighboring galaxies. Conversely, if a galaxy is found to be moving away from us at speed of 100,000 km/s based on its red shift, it is at a distance
This last calculation is approximate because it assumes the expansion rate was the same 5 billion years ago as it is now.
Scientists who study the origin, evolution, and ultimate fate of the universe ( cosmology ) believe that the universe began in an explosion, called the Big Bang , approximately 13.7 billion years ago. This explosion was not an explosion of particles through space, like fireworks, but a rapid expansion of space itself. The distances and velocities of the outward-going stars and galaxies permit us to estimate when all matter in the universe was once together—at the beginning of time.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?