| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A good-quality mirror may reflect more than of the light that falls on it, absorbing the rest. But it would be useful to have a mirror that reflects all of the light that falls on it. Interestingly, we can produce total reflection using an aspect of refraction.
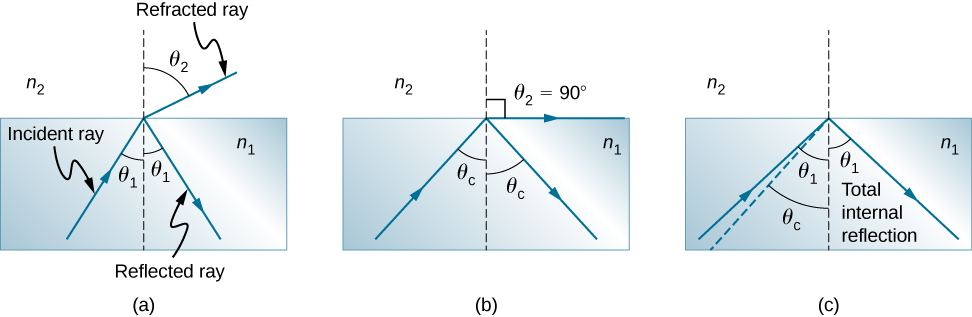
Consider what happens when a ray of light strikes the surface between two materials, as shown in [link] (a). Part of the light crosses the boundary and is refracted; the rest is reflected. If, as shown in the figure, the index of refraction for the second medium is less than for the first, the ray bends away from the perpendicular. (Since the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence—that is, Now imagine what happens as the incident angle increases. This causes to increase also. The largest the angle of refraction can be is , as shown in part (b). The critical angle for a combination of materials is defined to be the incident angle that produces an angle of refraction of . That is, is the incident angle for which . If the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, as shown in [link] (c), then all of the light is reflected back into medium 1, a condition called total internal reflection . (As the figure shows, the reflected rays obey the law of reflection so that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence in all three cases.)
Snell’s law states the relationship between angles and indices of refraction. It is given by
When the incident angle equals the critical angle , the angle of refraction is . Noting that Snell’s law in this case becomes
The critical angle for a given combination of materials is thus
Total internal reflection occurs for any incident angle greater than the critical angle , and it can only occur when the second medium has an index of refraction less than the first. Note that this equation is written for a light ray that travels in medium 1 and reflects from medium 2, as shown in [link] .
to find the critical angle where and

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?