| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding What would the electric field look like in a system with two parallel positively charged planes with equal charge densities?
The electric field would be zero in between, and have magnitude everywhere else.
Give a plausible argument as to why the electric field outside an infinite charged sheet is constant.
At infinity, we would expect the field to go to zero, but because the sheet is infinite in extent, this is not the case. Everywhere you are, you see an infinite plane in all directions.
Compare the electric fields of an infinite sheet of charge, an infinite, charged conducting plate, and infinite, oppositely charged parallel plates.
Describe the electric fields of an infinite charged plate and of two infinite, charged parallel plates in terms of the electric field of an infinite sheet of charge.
The infinite charged plate would have everywhere. The field would point toward the plate if it were negatively charged and point away from the plate if it were positively charged. The electric field of the parallel plates would be zero between them if they had the same charge, and E would be everywhere else. If the charges were opposite, the situation is reversed, zero outside the plates and between them.
A negative charge is placed at the center of a ring of uniform positive charge. What is the motion (if any) of the charge? What if the charge were placed at a point on the axis of the ring other than the center?
A thin conducting plate 1.0 m on the side is given a charge of . An electron is placed 1.0 cm above the center of the plate. What is the acceleration of the electron?
Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electric field 2.0 m from a long wire that is charged uniformly at
Two thin conducting plates, each 25.0 cm on a side, are situated parallel to one another and 5.0 mm apart. If electrons are moved from one plate to the other, what is the electric field between the plates?
The charge per unit length on the thin rod shown below is . What is the electric field at the point P ? ( Hint : Solve this problem by first considering the electric field at P due to a small segment dx of the rod, which contains charge . Then find the net field by integrating over the length of the rod.)

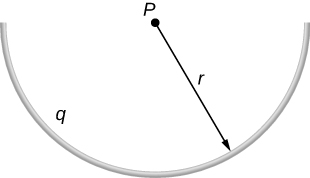
The charge per unit length on the thin semicircular wire shown below is . What is the electric field at the point P ?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?