| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding A thin straight wire has a uniform linear charge density Find the electric field at a distance d from the wire, where d is much less than the length of the wire.
; This agrees with the calculation of [link] where we found the electric field by integrating over the charged wire. Notice how much simpler the calculation of this electric field is with Gauss’s law.
A planar symmetry of charge density is obtained when charges are uniformly spread over a large flat surface. In planar symmetry, all points in a plane parallel to the plane of charge are identical with respect to the charges.
We take the plane of the charge distribution to be the xy -plane and we find the electric field at a space point P with coordinates ( x , y , z ). Since the charge density is the same at all ( x , y )-coordinates in the plane, by symmetry, the electric field at P cannot depend on the x - or y -coordinates of point P , as shown in [link] . Therefore, the electric field at P can only depend on the distance from the plane and has a direction either toward the plane or away from the plane. That is, the electric field at P has only a nonzero z -component.
Uniform charges in xy plane:
where z is the distance from the plane and is the unit vector normal to the plane. Note that in this system, although of course they point in opposite directions.
In the present case, a convenient Gaussian surface is a box, since the expected electric field points in one direction only. To keep the Gaussian box symmetrical about the plane of charges, we take it to straddle the plane of the charges, such that one face containing the field point P is taken parallel to the plane of the charges. In [link] , sides I and II of the Gaussian surface (the box) that are parallel to the infinite plane have been shaded. They are the only surfaces that give rise to nonzero flux because the electric field and the area vectors of the other faces are perpendicular to each other.
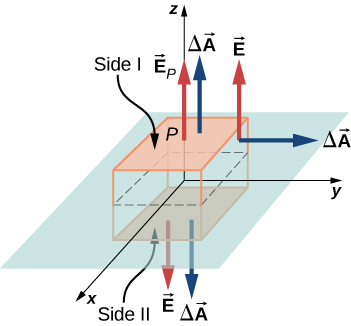
Let A be the area of the shaded surface on each side of the plane and be the magnitude of the electric field at point P . Since sides I and II are at the same distance from the plane, the electric field has the same magnitude at points in these planes, although the directions of the electric field at these points in the two planes are opposite to each other.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?