| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
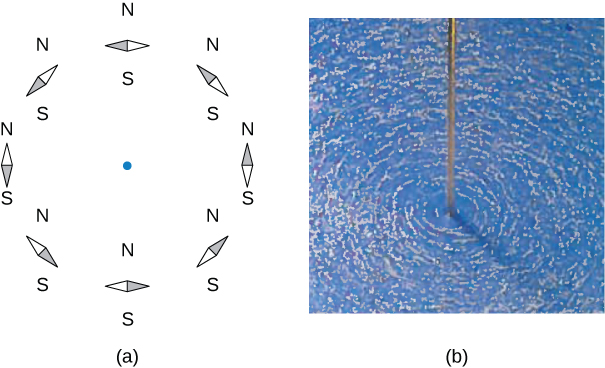
The direction of the field lines can be observed experimentally by placing several small compass needles on a circle near the wire, as illustrated in [link] . When there is no current in the wire, the needles align with Earth’s magnetic field. However, when a large current is sent through the wire, the compass needles all point tangent to the circle. Iron filings sprinkled on a horizontal surface also delineate the field lines, as shown in [link] .
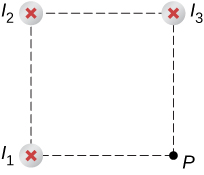
Wire 2 has a longer distance and a magnetic field contribution at point P of:
The vectors for each of these magnetic field contributions are shown.
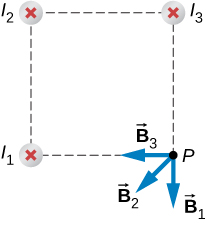
The magnetic field in the x -direction has contributions from wire 3 and the x -component of wire 2:
The y -component is similarly the contributions from wire 1 and the y -component of wire 2:
Therefore, the net magnetic field is the resultant of these two components:
Check Your Understanding Using [link] , keeping the currents the same in wires 1 and 3, what should the current be in wire 2 to counteract the magnetic fields from wires 1 and 3 so that there is no net magnetic field at point P?
4 amps flowing out of the page
How would you orient two long, straight, current-carrying wires so that there is no net magnetic force between them? ( Hint : What orientation would lead to one wire not experiencing a magnetic field from the other?)
You would make sure the currents flow perpendicular to one another.
A typical current in a lightning bolt is A. Estimate the magnetic field 1 m from the bolt.
The magnitude of the magnetic field 50 cm from a long, thin, straight wire is What is the current through the long wire?
20 A
A transmission line strung 7.0 m above the ground carries a current of 500 A. What is the magnetic field on the ground directly below the wire? Compare your answer with the magnetic field of Earth.
A long, straight, horizontal wire carries a left-to-right current of 20 A. If the wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude that is directed vertically downward, what is the resultant magnitude of the magnetic field 20 cm above the wire? 20 cm below the wire?
Both answers have the magnitude of magnetic field of
The two long, parallel wires shown in the accompanying figure carry currents in the same direction. If and what is the magnetic field at point P?
The accompanying figure shows two long, straight, horizontal wires that are parallel and a distance 2 a apart. If both wires carry current I in the same direction, (a) what is the magnetic field at (b)
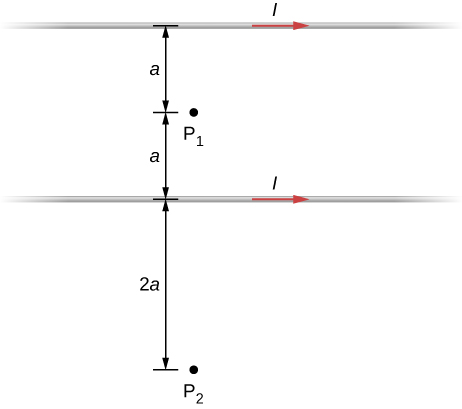
At P1, the net magnetic field is zero. At P2, into the page.
Repeat the calculations of the preceding problem with the direction of the current in the lower wire reversed.
Consider the area between the wires of the preceding problem. At what distance from the top wire is the net magnetic field a minimum? Assume that the currents are equal and flow in opposite directions.
The magnetic field is at a minimum at distance a from the top wire, or half-way between the wires.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?