| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A vector field (not necessarily an electric field; note units) is given by Calculate where S is the area shown below. Assume that
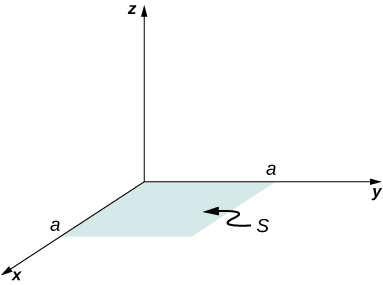
A circular area S is concentric with the origin, has radius a , and lies in the yz -plane. Calculate for
(a) Calculate the electric flux through the open hemispherical surface due to the electric field (see below). (b) If the hemisphere is rotated by around the x -axis, what is the flux through it?
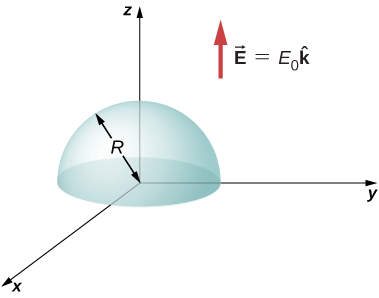
a. ; b. zero, since the flux through the upper half cancels the flux through the lower half of the sphere
Suppose that the electric field of an isolated point charge were proportional to rather than Determine the flux that passes through the surface of a sphere of radius R centered at the charge. Would Gauss’s law remain valid?
The electric field in a region is given by where and What is the net charge enclosed by the shaded volume shown below?
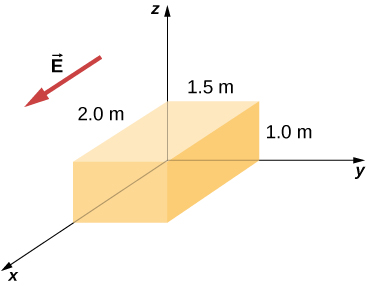
; There are two contributions to the surface integral: one at the side of the rectangle at
and the other at the side at
;
where the minus sign indicates that at
, the electric field is along positive
x and the unit normal is along negative
x . At
, the unit normal and the electric field vector are in the same direction:
.
Two equal and opposite charges of magnitude Q are located on the x -axis at the points + a and – a , as shown below. What is the net flux due to these charges through a square surface of side 2 a that lies in the yz -plane and is centered at the origin? ( Hint: Determine the flux due to each charge separately, then use the principle of superposition. You may be able to make a symmetry argument.)
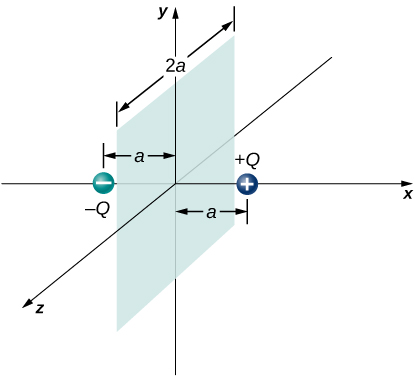
A fellow student calculated the flux through the square for the system in the preceding problem and got 0. What went wrong?
didn’t keep consistent directions for the area vectors, or the electric fields
A piece of aluminum foil of 0.1 mm thickness has a charge of that spreads on both wide side surfaces evenly. You may ignore the charges on the thin sides of the edges. (a) Find the charge density. (b) Find the electric field 1 cm from the center, assuming approximate planar symmetry.
Two pieces of aluminum foil of thickness 0.1 mm face each other with a separation of 5 mm. One of the foils has a charge of and the other has . (a) Find the charge density at all surfaces, i.e., on those facing each other and those facing away. (b) Find the electric field between the plates near the center assuming planar symmetry.
a. , on one and on the other; b.
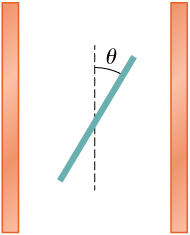
Two large copper plates facing each other have charge densities on the surface facing the other plate, and zero in between the plates. Find the electric flux through a rectangular area between the plates, as shown below, for the following orientations of the area. (a) If the area is parallel to the plates, and (b) if the area is tilted from the parallel direction. Note, this angle can also be

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?