| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding In [link] , the drift velocity was calculated for a 2.053-mm diameter (12-gauge) copper wire carrying a 20-amp current. Would the drift velocity change for a 1.628-mm diameter (14-gauge) wire carrying the same 20-amp current?
The diameter of the 14-gauge wire is smaller than the diameter of the 12-gauge wire. Since the drift velocity is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area, the drift velocity in the 14-gauge wire is larger than the drift velocity in the 12-gauge wire carrying the same current. The number of electrons per cubic meter will remain constant.
Although it is often convenient to attach a negative or positive sign to indicate the overall direction of motion of the charges, current is a scalar quantity, . It is often necessary to discuss the details of the motion of the charge, instead of discussing the overall motion of the charges. In such cases, it is necessary to discuss the current density, , a vector quantity. The current density is the flow of charge through an infinitesimal area, divided by the area. The current density must take into account the local magnitude and direction of the charge flow, which varies from point to point. The unit of current density is ampere per meter squared, and the direction is defined as the direction of net flow of positive charges through the area.
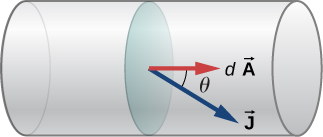
The relationship between the current and the current density can be seen in [link] . The differential current flow through the area is found as
where is the angle between the area and the current density. The total current passing through area can be found by integrating over the area,
Consider the magnitude of the current density, which is the current divided by the area:
Thus, the current density is . If q is positive, is in the same direction as the electrical field . If q is negative, is in the opposite direction of . Either way, the direction of the current density is in the direction of the electrical field .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?