| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
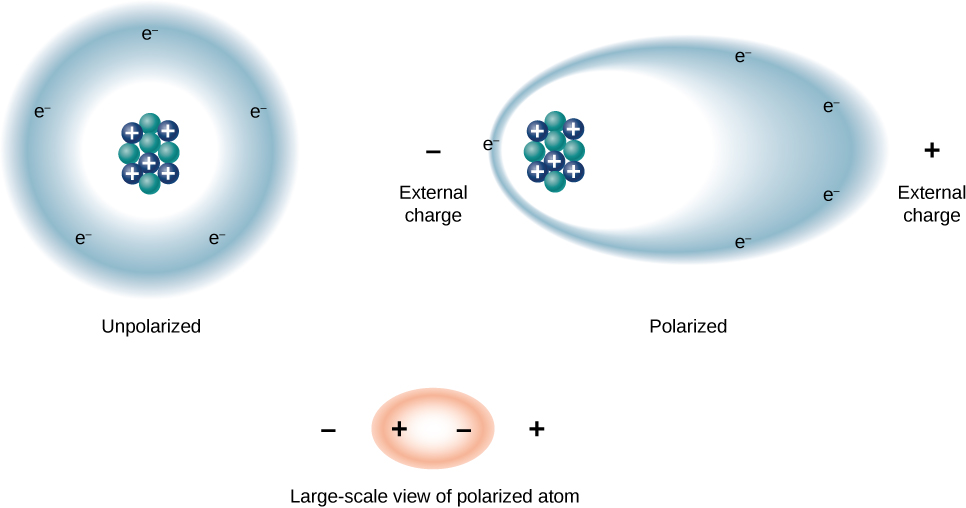
We can understand the effect of a dielectric on capacitance by looking at its behavior at the molecular level. As we have seen in earlier chapters, in general, all molecules can be classified as either polar or nonpolar . There is a net separation of positive and negative charges in an isolated polar molecule, whereas there is no charge separation in an isolated nonpolar molecule ( [link] ). In other words, polar molecules have permanent electric-dipole moments and nonpolar molecules do not. For example, a molecule of water is polar, and a molecule of oxygen is nonpolar. Nonpolar molecules can become polar in the presence of an external electrical field, which is called induced polarization .
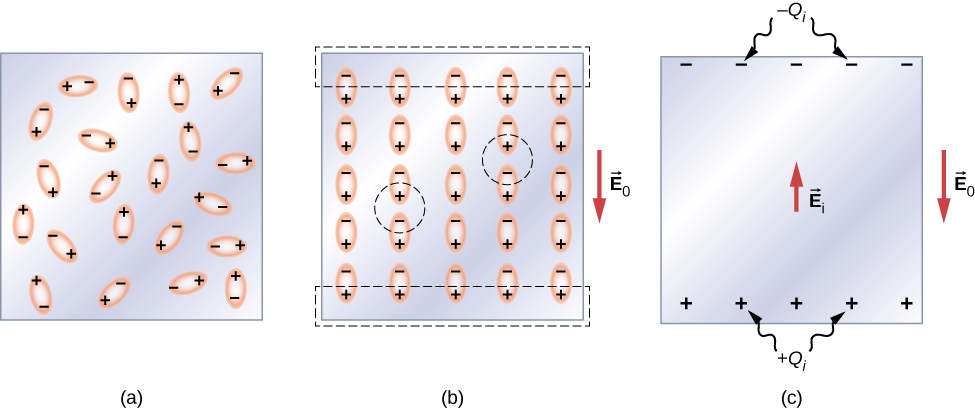
Let’s first consider a dielectric composed of polar molecules. In the absence of any external electrical field, the electric dipoles are oriented randomly, as illustrated in [link] (a). However, if the dielectric is placed in an external electrical field , the polar molecules align with the external field, as shown in part (b) of the figure. Opposite charges on adjacent dipoles within the volume of dielectric neutralize each other, so there is no net charge within the dielectric (see the dashed circles in part (b)). However, this is not the case very close to the upper and lower surfaces that border the dielectric (the region enclosed by the dashed rectangles in part (b)), where the alignment does produce a net charge. Since the external electrical field merely aligns the dipoles, the dielectric as a whole is neutral, and the surface charges induced on its opposite faces are equal and opposite. These induced surface charges and produce an additional electrical field (an induced electrical field ), which opposes the external field , as illustrated in part (c).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?