| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Because a conductor is an equipotential, it can replace any equipotential surface. For example, in [link] , a charged spherical conductor can replace the point charge, and the electric field and potential surfaces outside of it will be unchanged, confirming the contention that a spherical charge distribution is equivalent to a point charge at its center.
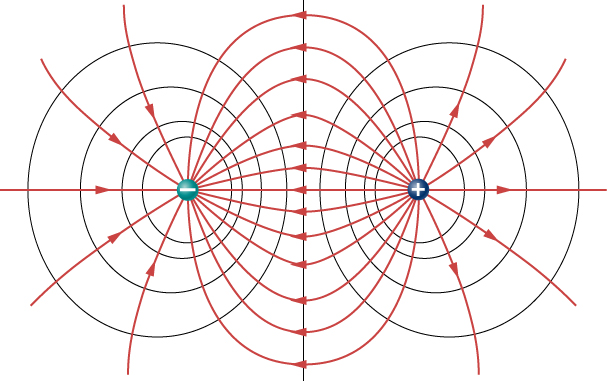
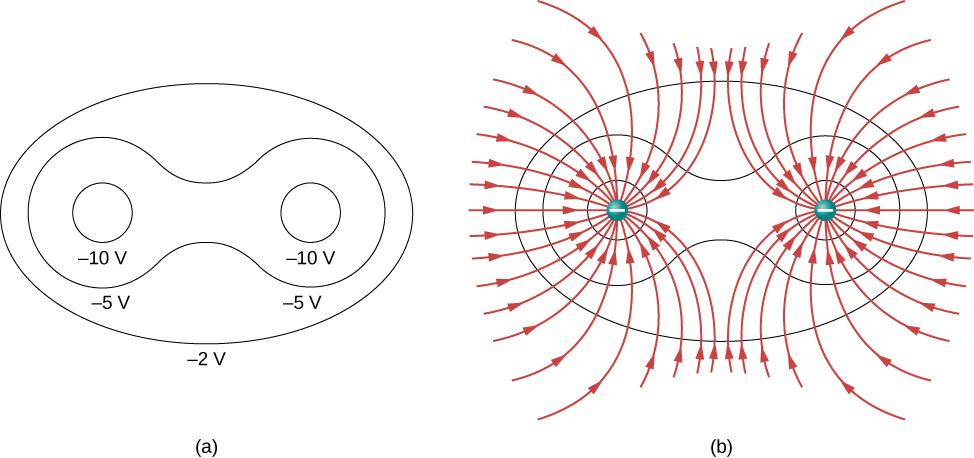
[link] shows the electric field and equipotential lines for two equal and opposite charges. Given the electric field lines, the equipotential lines can be drawn simply by making them perpendicular to the electric field lines. Conversely, given the equipotential lines, as in [link] (a), the electric field lines can be drawn by making them perpendicular to the equipotentials, as in [link] (b).
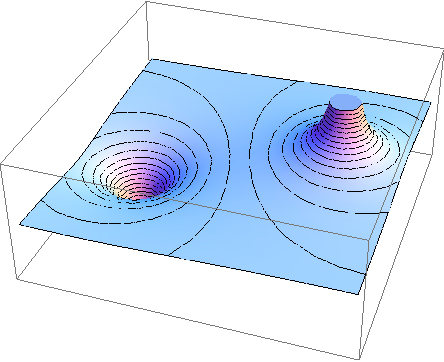
To improve your intuition, we show a three-dimensional variant of the potential in a system with two opposing charges. [link] displays a three-dimensional map of electric potential, where lines on the map are for equipotential surfaces. The hill is at the positive charge, and the trough is at the negative charge. The potential is zero far away from the charges. Note that the cut off at a particular potential implies that the charges are on conducting spheres with a finite radius.
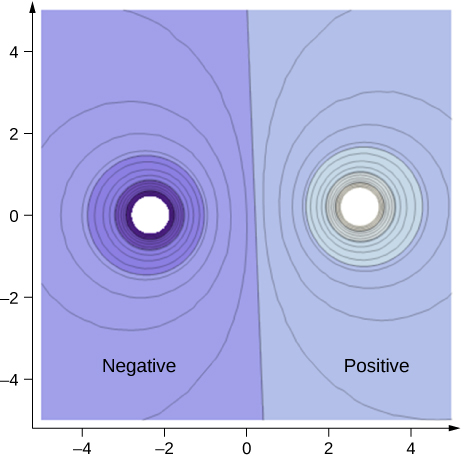
A two-dimensional map of the cross-sectional plane that contains both charges is shown in [link] . The line that is equidistant from the two opposite charges corresponds to zero potential, since at the points on the line, the positive potential from the positive charge cancels the negative potential from the negative charge. Equipotential lines in the cross-sectional plane are closed loops, which are not necessarily circles, since at each point, the net potential is the sum of the potentials from each charge.
View this simulation to observe and modify the equipotential surfaces and electric fields for many standard charge configurations. There’s a lot to explore.
One of the most important cases is that of the familiar parallel conducting plates shown in [link] . Between the plates, the equipotentials are evenly spaced and parallel. The same field could be maintained by placing conducting plates at the equipotential lines at the potentials shown.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?