| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
So far, we have generally been working with charges occupying a volume within an insulator. We now study what happens when free charges are placed on a conductor. Generally, in the presence of a (generally external) electric field, the free charge in a conductor redistributes and very quickly reaches electrostatic equilibrium. The resulting charge distribution and its electric field have many interesting properties, which we can investigate with the help of Gauss’s law and the concept of electric potential.
If an electric field is present inside a conductor, it exerts forces on the free electrons (also called conduction electrons), which are electrons in the material that are not bound to an atom. These free electrons then accelerate. However, moving charges by definition means nonstatic conditions, contrary to our assumption. Therefore, when electrostatic equilibrium is reached, the charge is distributed in such a way that the electric field inside the conductor vanishes.
If you place a piece of a metal near a positive charge, the free electrons in the metal are attracted to the external positive charge and migrate freely toward that region. The region the electrons move to then has an excess of electrons over the protons in the atoms and the region from where the electrons have migrated has more protons than electrons. Consequently, the metal develops a negative region near the charge and a positive region at the far end ( [link] ). As we saw in the preceding chapter, this separation of equal magnitude and opposite type of electric charge is called polarization . If you remove the external charge, the electrons migrate back and neutralize the positive region.
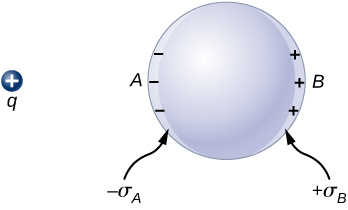
The polarization of the metal happens only in the presence of external charges. You can think of this in terms of electric fields. The external charge creates an external electric field. When the metal is placed in the region of this electric field, the electrons and protons of the metal experience electric forces due to this external electric field, but only the conduction electrons are free to move in the metal over macroscopic distances. The movement of the conduction electrons leads to the polarization, which creates an induced electric field in addition to the external electric field ( [link] ). The net electric field is a vector sum of the fields of and the surface charge densities and This means that the net field inside the conductor is different from the field outside the conductor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?