| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You are certainly familiar with electronic devices that you activate with the click of a switch, from computers to cell phones to television. And you have certainly seen electricity in a flash of lightning during a heavy thunderstorm. But you have also most likely experienced electrical effects in other ways, maybe without realizing that an electric force was involved. Let’s take a look at some of these activities and see what we can learn from them about electric charges and forces.
You have probably experienced the phenomenon of static electricity : When you first take clothes out of a dryer, many (not all) of them tend to stick together; for some fabrics, they can be very difficult to separate. Another example occurs if you take a woolen sweater off quickly—you can feel (and hear) the static electricity pulling on your clothes, and perhaps even your hair. If you comb your hair on a dry day and then put the comb close to a thin stream of water coming out of a faucet, you will find that the water stream bends toward (is attracted to) the comb ( [link] ).
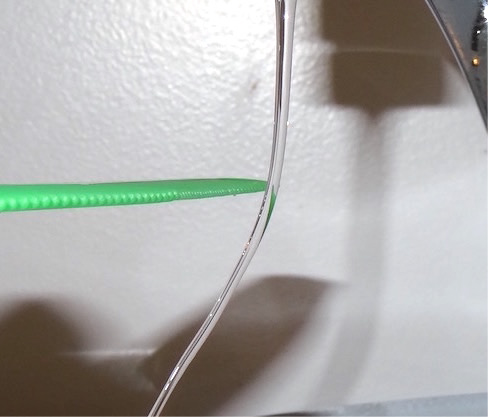
Suppose you bring the comb close to some small strips of paper; the strips of paper are attracted to the comb and even cling to it ( [link] ). In the kitchen, quickly pull a length of plastic cling wrap off the roll; it will tend to cling to most any nonmetallic material (such as plastic, glass, or food). If you rub a balloon on a wall for a few seconds, it will stick to the wall. Probably the most annoying effect of static electricity is getting shocked by a doorknob (or a friend) after shuffling your feet on some types of carpeting.

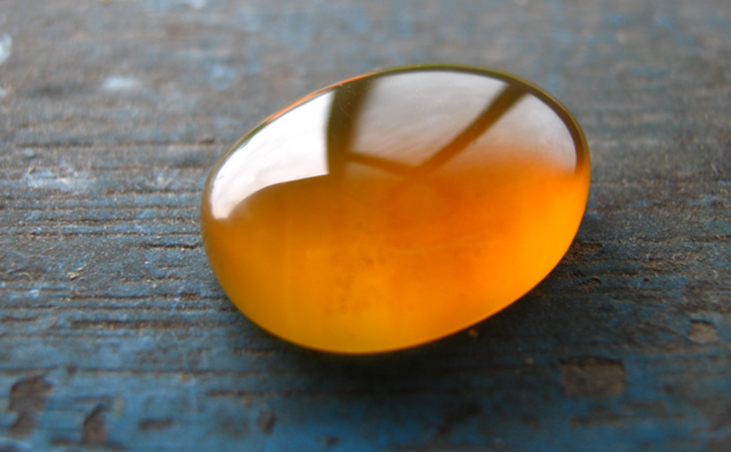
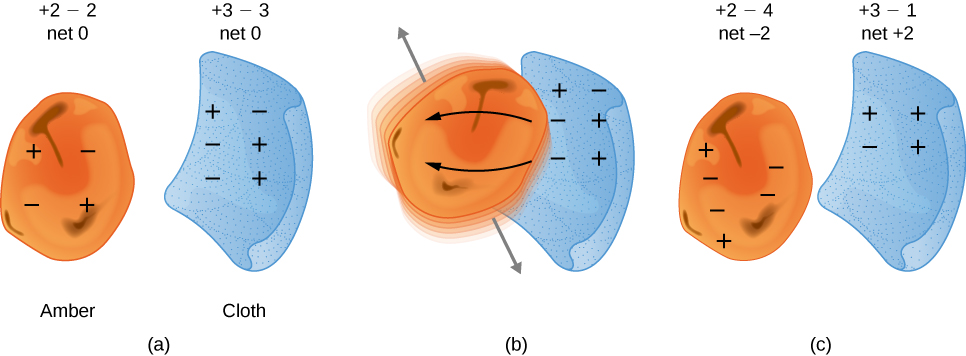
Many of these phenomena have been known for centuries. The ancient Greek philosopher Thales of Miletus (624–546 BCE) recorded that when amber (a hard, translucent, fossilized resin from extinct trees) was vigorously rubbed with a piece of fur, a force was created that caused the fur and the amber to be attracted to each other ( [link] ). Additionally, he found that the rubbed amber would not only attract the fur, and the fur attract the amber, but they both could affect other (nonmetallic) objects, even if not in contact with those objects ( [link] ).


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?