| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Material objects consist of charged particles. An electromagnetic wave incident on the object exerts forces on the charged particles, in accordance with the Lorentz force, [link] . These forces do work on the particles of the object, increasing its energy, as discussed in the previous section. The energy that sunlight carries is a familiar part of every warm sunny day. A much less familiar feature of electromagnetic radiation is the extremely weak pressure that electromagnetic radiation produces by exerting a force in the direction of the wave. This force occurs because electromagnetic waves contain and transport momentum.
To understand the direction of the force for a very specific case, consider a plane electromagnetic wave incident on a metal in which electron motion, as part of a current, is damped by the resistance of the metal, so that the average electron motion is in phase with the force causing it. This is comparable to an object moving against friction and stopping as soon as the force pushing it stops ( [link] ). When the electric field is in the direction of the positive y -axis, electrons move in the negative y -direction, with the magnetic field in the direction of the positive z -axis. By applying the right-hand rule, and accounting for the negative charge of the electron, we can see that the force on the electron from the magnetic field is in the direction of the positive x -axis, which is the direction of wave propagation. When the E field reverses, the B field does too, and the force is again in the same direction. Maxwell’s equations together with the Lorentz force equation imply the existence of radiation pressure much more generally than this specific example, however.
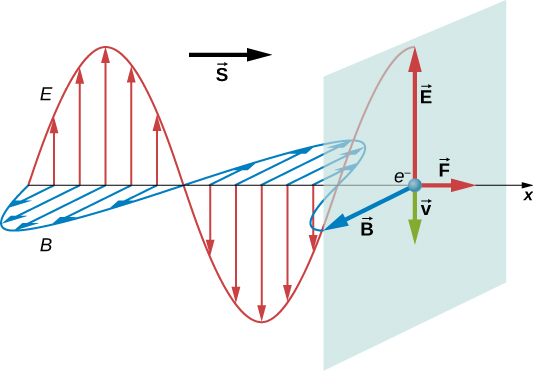
Maxwell predicted that an electromagnetic wave carries momentum. An object absorbing an electromagnetic wave would experience a force in the direction of propagation of the wave. The force corresponds to radiation pressure exerted on the object by the wave. The force would be twice as great if the radiation were reflected rather than absorbed.
Maxwell’s prediction was confirmed in 1903 by Nichols and Hull by precisely measuring radiation pressures with a torsion balance. The schematic arrangement is shown in [link] . The mirrors suspended from a fiber were housed inside a glass container. Nichols and Hull were able to obtain a small measurable deflection of the mirrors from shining light on one of them. From the measured deflection, they could calculate the unbalanced force on the mirror, and obtained agreement with the predicted value of the force.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?