| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Anyone who has used a microwave oven knows there is energy in electromagnetic waves. Sometimes this energy is obvious, such as in the warmth of the summer Sun. Other times, it is subtle, such as the unfelt energy of gamma rays, which can destroy living cells.
Electromagnetic waves bring energy into a system by virtue of their electric and magnetic fields. These fields can exert forces and move charges in the system and, thus, do work on them. However, there is energy in an electromagnetic wave itself, whether it is absorbed or not. Once created, the fields carry energy away from a source. If some energy is later absorbed, the field strengths are diminished and anything left travels on.
Clearly, the larger the strength of the electric and magnetic fields, the more work they can do and the greater the energy the electromagnetic wave carries. In electromagnetic waves, the amplitude is the maximum field strength of the electric and magnetic fields ( [link] ). The wave energy is determined by the wave amplitude.
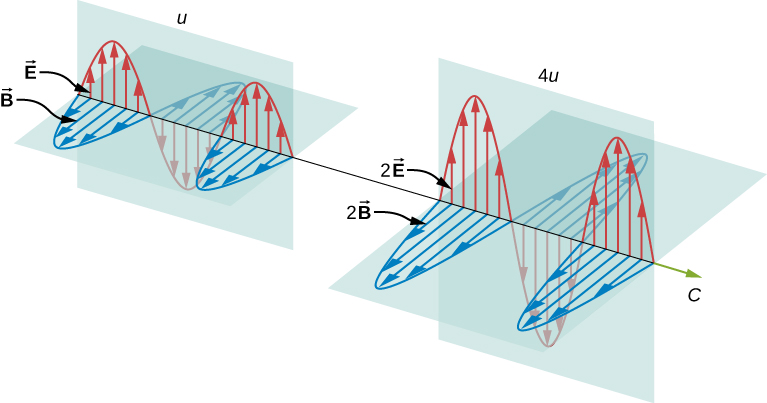
For a plane wave traveling in the direction of the positive x -axis with the phase of the wave chosen so that the wave maximum is at the origin at , the electric and magnetic fields obey the equations
The energy in any part of the electromagnetic wave is the sum of the energies of the electric and magnetic fields. This energy per unit volume, or energy density u , is the sum of the energy density from the electric field and the energy density from the magnetic field. Expressions for both field energy densities were discussed earlier ( in Capacitance and in Inductance ). Combining these the contributions, we obtain
The expression then shows that the magnetic energy density and electric energy density are equal, despite the fact that changing electric fields generally produce only small magnetic fields. The equality of the electric and magnetic energy densities leads to
The energy density moves with the electric and magnetic fields in a similar manner to the waves themselves.
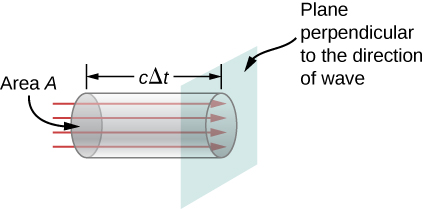
We can find the rate of transport of energy by considering a small time interval . As shown in [link] , the energy contained in a cylinder of length and cross-sectional area A passes through the cross-sectional plane in the interval

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?