| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inductance is the property of a device that tells us how effectively it induces an emf in another device. In other words, it is a physical quantity that expresses the effectiveness of a given device.
When two circuits carrying time-varying currents are close to one another, the magnetic flux through each circuit varies because of the changing current I in the other circuit. Consequently, an emf is induced in each circuit by the changing current in the other. This type of emf is therefore called a mutually induced emf , and the phenomenon that occurs is known as mutual inductance ( M ) . As an example, let’s consider two tightly wound coils ( [link] ). Coils 1 and 2 have and turns and carry currents and respectively. The flux through a single turn of coil 2 produced by the magnetic field of the current in coil 1 is whereas the flux through a single turn of coil 1 due to the magnetic field of is
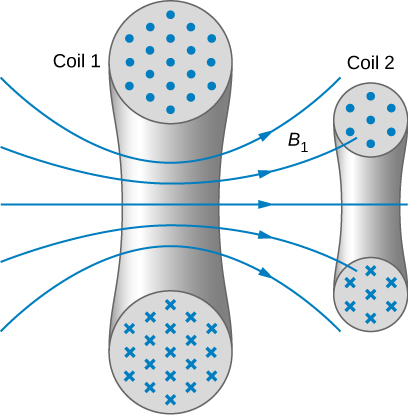
The mutual inductance of coil 2 with respect to coil 1 is the ratio of the flux through the turns of coil 2 produced by the magnetic field of the current in coil 1, divided by that current, that is,
Similarly, the mutual inductance of coil 1 with respect to coil 2 is
Like capacitance, mutual inductance is a geometric quantity. It depends on the shapes and relative positions of the two coils, and it is independent of the currents in the coils. The SI unit for mutual inductance M is called the henry (H) in honor of Joseph Henry (1799–1878), an American scientist who discovered induced emf independently of Faraday. Thus, we have . From [link] and [link] , we can show that so we usually drop the subscripts associated with mutual inductance and write
The emf developed in either coil is found by combining Faraday’s law and the definition of mutual inductance. Since is the total flux through coil 2 due to , we obtain
where we have used the fact that M is a time-independent constant because the geometry is time-independent. Similarly, we have
In [link] , we can see the significance of the earlier description of mutual inductance ( M ) as a geometric quantity. The value of M neatly encapsulates the physical properties of circuit elements and allows us to separate the physical layout of the circuit from the dynamic quantities, such as the emf and the current. [link] defines the mutual inductance in terms of properties in the circuit, whereas the previous definition of mutual inductance in [link] is defined in terms of the magnetic flux experienced, regardless of circuit elements. You should be careful when using [link] and [link] because do not necessarily represent the total emfs in the respective coils. Each coil can also have an emf induced in it because of its self-inductance (self-inductance will be discussed in more detail in a later section).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?