-
Home
- University physics volume 2
- Unit 2. electricity and magnetism
- Electromagnetic induction
- Induced electric fields
Summary
- A changing magnetic flux induces an electric field.
- Both the changing magnetic flux and the induced electric field are related to the induced emf from Faraday’s law.
Conceptual questions
Is the work required to accelerate a rod from rest to a speed
v in a magnetic field greater than the final kinetic energy of the rod? Why?
The work is greater than the kinetic energy because it takes energy to counteract the induced emf.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
The copper sheet shown below is partially in a magnetic field. When it is pulled to the right, a resisting force pulls it to the left. Explain. What happen if the sheet is pushed to the left?
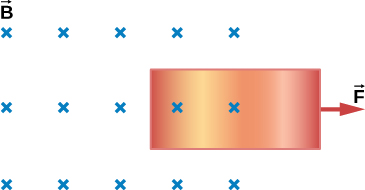
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Problems
Calculate the induced electric field in a 50-turn coil with a diameter of 15 cm that is placed in a spatially uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.50 T so that the face of the coil and the magnetic field are perpendicular. This magnetic field is reduced to zero in 0.10 seconds. Assume that the magnetic field is cylindrically symmetric with respect to the central axis of the coil.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
The magnetic field through a circular loop of radius 10.0 cm varies with time as shown in the accompanying figure. The field is perpendicular to the loop. Assuming cylindrical symmetry with respect to the central axis of the loop, plot the induced electric field in the loop as a function of time.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
The current
I through a long solenoid with
n turns per meter and radius
R is changing with time as given by
dI /
dt . Calculate the induced electric field as a function of distance
r from the central axis of the solenoid.
Inside,
so,
(inside). Outside,
so,
(outside)
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Over a region of radius
R , there is a spatially uniform magnetic field
(See below.) At
,
after which it decreases at a constant rate to zero in 30 s. (a) What is the electric field in the regions where
and
during that 30-s interval? (b) Assume that
. How much work is done by the electric field on a proton that is carried once clock wise around a circular path of radius 5.0 cm? (c) How much work is done by the electric field on a proton that is carried once counterclockwise around a circular path of any radius
? (d) At the instant when
, a proton enters the magnetic field at
A , moving a velocity
as shown. What are the electric and magnetic forces on the proton at that instant?
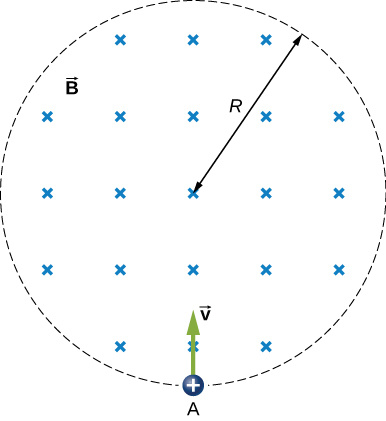
a.
,
; b.
; c. 0 J; d.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
The magnetic field at all points within the cylindrical region whose cross-section is indicated in the accompanying figure starts at 1.0 T and decreases uniformly to zero in 20 s. What is the electric field (both magnitude and direction) as a function of
r , the distance from the geometric center of the region?
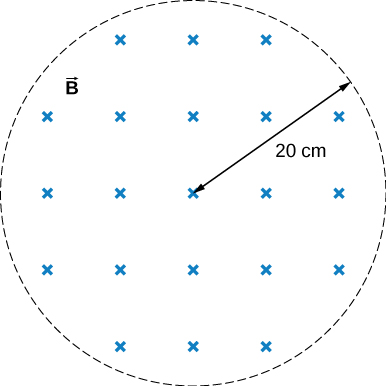
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
The current in a long solenoid of radius 3 cm is varied with time at a rate of 2 A/s. A circular loop of wire of radius 5 cm and resistance
surrounds the solenoid. Find the electrical current induced in the loop.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
The current in a long solenoid of radius 3 cm and 20 turns/cm is varied with time at a rate of 2 A/s. Find the electric field at a distance of 4 cm from the center of the solenoid.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Questions & Answers
how does Neisseria cause meningitis
is the branch of biology that deals with the study of microorganisms.
studies of microbes
Louisiaste
when we takee the specimen which lumbar,spin,
How bacteria create energy to survive?
Bacteria doesn't produce energy they are dependent upon their substrate in case of lack of nutrients they are able to make spores which helps them to sustain in harsh environments
_Adnan
But not all bacteria make spores, l mean Eukaryotic cells have Mitochondria which acts as powerhouse for them, since bacteria don't have it, what is the substitution for it?
Muhamad
they make spores
Louisiaste
what is sporadic nd endemic, epidemic
the significance of food webs for disease transmission
Abreham
food webs brings about an infection as an individual depends on number of diseased foods or carriers dully.
Mark
explain assimilatory nitrate reduction
Assimilatory nitrate reduction is a process that occurs in some microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, in which nitrate (NO3-) is reduced to nitrite (NO2-), and then further reduced to ammonia (NH3).
Elkana
This process is called assimilatory nitrate reduction because the nitrogen that is produced is incorporated in the cells of microorganisms where it can be used in the synthesis of amino acids and other nitrogen products
Elkana
Examples of thermophilic organisms
Give Examples of thermophilic organisms
Shu
advantages of normal Flora to the host
Prevent foreign microbes to the host
Abubakar
they provide healthier benefits to their hosts
ayesha
They are friends to host only when Host immune system is strong and become enemies when the host immune system is weakened . very bad relationship!
Mark
cell is the smallest unit of life
Fauziya
cell is the smallest unit of life
Akanni
cell is the structural and functional unit of life
Hasan
is the fundamental units of Life
Musa
what are emergency diseases
There are nothing like emergency disease but there are some common medical emergency which can occur simultaneously like Bleeding,heart attack,Breathing difficulties,severe pain heart stock.Hope you will get my point .Have a nice day ❣️
_Adnan
define infection ,prevention and control
Innocent
I think infection prevention and control is the avoidance of all things we do that gives out break of infections and promotion of health practices that promote life
Lubega
Heyy Lubega hussein where are u from?
_Adnan
which site have a normal flora
Many sites of the body have it
Skin
Nasal cavity
Oral cavity
Gastro intestinal tract
Safaa
skin,Oral,Nasal,GIt
Sadik
How can Commensal can Bacteria change into pathogen?
Sadik
How can Commensal Bacteria change into pathogen?
Sadik
what are the advantages of normal Flora to the host
Micheal
what are the ways of control and prevention of nosocomial infection in the hospital
Micheal
part of a tissue or an organ being wounded or bruised.
Wilfred
what term is used to name and classify microorganisms?
Binomial nomenclature
adeolu
Got questions? Join the online conversation and get instant answers!
Source:
OpenStax, University physics volume 2. OpenStax CNX. Oct 06, 2016 Download for free at http://cnx.org/content/col12074/1.3
Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google Inc.



